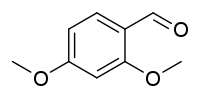
2,4-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde
2,4-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde (DMBA) is a reagent used to specifically quantify phlorotannins. This product reacts specifically with 1,3-and 1,3,5-substituted phenols (e.g., phlorotannins) to form a colored product.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,4-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.404 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 166.176 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 1.114 g/mL |
| Melting point | 67 °C (153 °F; 340 K) |
| Boiling point | 307.8 °C (586.0 °F; 581.0 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Stern, J. Lewis; Hagerman, Ann E.; Steinberg, Peter D.; Winter, Frank C.; Estes, James A. (1996). "A new assay for quantifying brown algal phlorotannins and comparisons to previous methods". Journal of Chemical Ecology. 22 (7): 1273–1293. doi:10.1007/BF02266965. PMID 24226084. S2CID 20164807.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.