2-Ethoxybenzoic acid
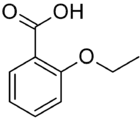
2-Ethoxybenzoic acid (o-ethoxybenzoic acid, EBA) is an organic compound, a carboxylic acid derived from benzoic acid. 2-Ethoxybenzoic acid is used as a component in some dental cements.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Ethoxybenzoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.665 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 166.176 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 19 °C (66 °F; 292 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Fischer Scientific |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Brauer, G.M.; Stansbury, J.W. (1984). "Materials Science Cements Containing Syringic Acid Esters- o-Ethoxybenzoic Acid and Zinc Oxide". Journal of Dental Research. 63 (2): 137–140. doi:10.1177/00220345840630020801. PMID 6363481.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
