4,4'-Oxydianiline
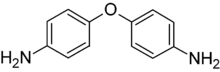
4,4’-Oxydianiline is an organic compound with the formula O(C6H4NH2)2. It is an ether derivative of aniline. This colourless solid is a useful monomer and cross-linking agent for polymers, especially the polyimides, such as Kapton.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4,4'-oxydianiline | |
| Other names
4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether; 4-aminophenyl ether; 4,4'-oxybisbenzenamine; bis(4-aminophenyl) ether; 4,4'-ODA | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.707 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3077 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H12N2O | |
| Molar mass | 200.24 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless crystalline solid |
| Melting point | 188 to 192 °C (370 to 378 °F; 461 to 465 K) |
| Boiling point | 219 °C (426 °F; 492 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |    |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H311, H331, H340, H350, H361f, H411 | |
| P201, P202, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P281, P301+310, P302+352, P304+340, P308+313, P311, P312, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P391, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 219 °C (426 °F; 492 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Uses
4,4’-Oxydianiline is used in the production of a wide variety of polymer resins. The primary use lies in the production of polyimide and poly(ester)imide resins. These resins are used for their temperature-resistant properties and are utilized in products including wire enamels, coatings, film, adhesives, insulating varnishes, coated fabrics, flame-retardant fibers, oil sealants and retainers, insulation for cables and printed circuits, and laminates and composite for aerospace vehicles.
Other applications of 4,4’-oxydianiline include the production of poly(amide)imide resins (which are used in the manufacture of heat-resistant wire enamels and coatings), as an intermediate in the manufacture of epoxy resins and adhesives, and in the production of aromatic polyether imides.[1]
A specific reaction involving industrial use of 4,4’-oxydianiline is in the production of thermostable poly(amideurea) acids, which can be prepared from 4,4’-oxydianiline, pyromellitic dianhydride, and diisocyanates. These poly(amideurea) acids can be used as intermediates in the syntheses of poly(imideurea)s:[2]

References
- "11th ROC: 4,4'-Oxydianiline" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2009-01-31. Retrieved 2008-02-28.
- Chiria, C.I; Tanasã, F. (2000). "Polyureas". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. doi:10.1002/14356007.d21_d01. ISBN 3527306730.
External links
- MSDS Material Safety Data Sheet provided by Sigma-Aldrich.
