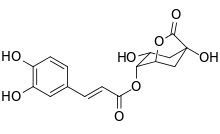
4-Caffeoyl-1,5-quinide
4-Caffeoyl-1,5-quinide (4-caffeoylquinic-1,5-lactone or 4-CQL) is found in roasted coffee beans. It is formed by lactonization of 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid during the roasting process.[1]
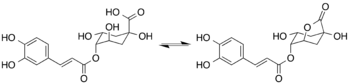 Lactonization of 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid during roasting to form of 4-CQL
Lactonization of 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid during roasting to form of 4-CQL
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
4-Caffeoylquinic-1,5-lactone; 4-CQL | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H16O8 | |
| Molar mass | 336.296 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is reported to possess opioid antagonist properties in mice.[2]
References
- Alan Crozier; Mike N. Clifford; Hiroshi Ashihara, eds. (2006). Plant Secondary Metabolites: Occurrence, Structure and Role in the Human Diet. Blackwell Publishing Ltd. p. 275.
- de Paulis, Tomas; Commers, Patricia; Farah, Adriana; Zhao, Jiali; McDonald, Michael P.; Galici, Ruggero; Martin, Peter R. (2004). "4-Caffeoyl-1,5-quinide in roasted coffee inhibits [3H]naloxone binding and reverses anti-nociceptive effects of morphine in mice" (PDF). Psychopharmacology. 176: 146–153. doi:10.1007/s00213-004-1876-9. PMID 15088081. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2013-05-29.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.