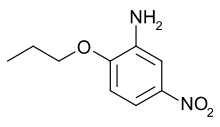
5-Nitro-2-propoxyaniline
5-Nitro-2-propoxyaniline, also known as P-4000 and Ultrasüss, is one of the strongest sweet-tasting substances known, about 4,000 times the intensity of sucrose (hence its alternate name, P-4000). It is an orange solid that is only slightly soluble in water. It is stable in boiling water and dilute acids. 5-Nitro-2-propoxyaniline was once used as an artificial sweetener but has been banned in the United States because of its possible toxicity.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5-Nitro-2-propoxyaniline | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.228 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H12N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 196.21 g/mol |
| Melting point | 48 °C (118 °F; 321 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
In the US, food containing any added or detectable level of 5-nitro-2-propoxyaniline is deemed to be adulterated in violation of the act based upon an order published in the Federal Register of January 19, 1950 (15 FR 321).[2]
References
- Merck Index, 12th Edition, 6727.
- FDA Code of Regulations
External links
 Media related to 5-Nitro-2-propoxyaniline at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to 5-Nitro-2-propoxyaniline at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.