ALC-0315
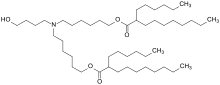
ALC-0315 (((4-Hydroxybutyl)azanediyl)bis(hexane-6,1-diyl)bis(2-hexyldecanoate)) is a component of the lipid mixture used in the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, BNT162b2, from BioNTech and Pfizer to form lipid nanoparticles.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
((4-hydroxybutyl)azanediyl)bis(hexane-6,1-diyl)bis(2-hexyldecanoate) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C48H95NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 766.290 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
ALC-0315 is a physiological pH cationic synthetic lipid that can be used together with other lipids to form lipid nanoparticles (LNPs).[1]
These nanoparticles promote the uptake of therapeutically effective nucleic acids such as oligonucleotides or messenger RNA both in vitro and in vivo. [2][3]
See also
References
- Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (11 December 2020). "Public Assessment Report: Authorisation for Temporary Supply COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine BNT162b2" (PDF).
- mRNA-based therapeutics — developing a new class of drugs, Ugur Sahin, Katalin Karikó and Özlem Türeci, Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 13, 759-780 (2014), doi:10.1038/nrd4278.
- mRNA vaccines — a new era in vaccinology, Norbert Pardi, Michael J. Hogan, Frederick W. Porter and Drew Weissman, Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 17, 261-279 (2018), doi:10.1038/nrd.2017.243.
External links
- WIPO patent WO 2018/081480 A1 - occurs as compound III-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.