Acetoacetanilide
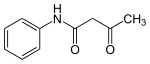
Acetoacetanilide is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2C(O)NHC6H5. It is the acetoacetamide derivative of aniline. It is a white solid that is poorly soluble in water. It and many related compounds (prepared from various aniline derivatives) are used in the production of organic pigments called arylide yellows.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Oxo-N-phenylbutanamide | |
| Other names
Acetoacetylaminobenzene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.725 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H11NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 177.203 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless solid |
| Melting point | 83 to 88 °C (181 to 190 °F; 356 to 361 K) |
| low | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H312, H332, H373 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P312, P314, P322, P330, P363, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Preparation and reactions
Acetoacetanilide is prepared by acetoacetylation of aniline using diketene.
To make the dyes, acetoacetanilides are coupled to diazonium salts, "azo coupling".[1]
See also
References
- K. Hunger. W. Herbst "Pigments, Organic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2012. doi:10.1002/14356007.a20_371
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
