Administrative divisions of Czechoslovakia
This article deals with historic administrative divisions of Czechoslovakia up to 1992, when the country was split into the Czech Republic and Slovakia and the divisions were changed.
For the current divisions of those two countries, see their main articles and the articles Regions of Slovakia and Regions of the Czech Republic.
Latest division (1960–1992)
The country consisted of 10 Regions ('kraje'), Prague, and (since 1970) Bratislava; further divided in 109–114 districts ('okresy').
The kraje were abolished temporarily in Slovakia in 1969–1970 and since late 1990 in whole Czechoslovakia. In addition, the two republics Czech Socialist Republic and Slovak Socialist Republic were established in 1969 during the federalization process. The word Socialist was removed from the republics' names in 1990 after the Velvet Revolution.
Since many regions changed significantly after the Velvet Divorce of 1993, here is list of their original names and current regions they approximately correspond to:
Czech (Socialist) Republic
(the names are in Czech)
- Praha
- Středočeský kraj: today Central Bohemian Region
- Jihočeský kraj: today South Bohemian Region
- Západočeský kraj (West Bohemian Region): today Plzeň Region and Karlovy Vary Region
- Severočeský kraj (North Bohemian Region): today Ústí nad Labem Region, and most of Liberec Region
- Východočeský kraj (East Bohemian Region): today Hradec Králové Region, Pardubice Region, and small parts of Liberec Region and Vysočina Region
- Jihomoravský kraj (South Moravian Region): today South Moravian Region, and most of Vysočina Region and Zlín Region
- Severomoravský kraj (North Moravian Region): today Moravian-Silesian Region, Olomouc Region, and part of Zlín Region
Slovak (Socialist) Republic
(the names are in Slovak)
- Bratislava: today a part of the Bratislava Region
- Západoslovenský kraj (West Slovak Region): Trnava Region, Nitra Region, most of Bratislava Region, and a small part of Trenčín Region
- Stredoslovenský kraj (Central Slovak Region): today Žilina Region, Banská Bystrica Region, and a large part of Trenčín Region
- Východoslovenský kraj (East Slovak Region): today Prešov Region and Košice Region
History
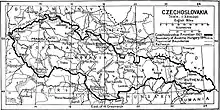


- 1918–1923: different systems based on former Austrian territories (Kingdom of Bohemia, Margraviate of Moravia, and Duchy of Upper and Lower Silesia) and former Hungarian counties in the north (later forming Slovakia (21 counties) and Subcarpathian Ruthenia (4 counties)) were reorganized into three provinces (Czech: země, Slovak: krajiny – literally "lands") of Bohemia-Moravia-Silesia, 21 counties (župy) of Slovakia, and 4 counties of Subcarpathian Ruthenia (today's Zakarpattia Oblast in Ukraine); all provinces and counties were further divided into districts (okresy)
- 1923–1927: like above, except that the above counties were replaced by 6 (grand) counties ((veľ)župy) in Slovakia and 1 (grand) county in Subcarpathian Ruthenia, and the number and frontiers of districts were changed on these two territories
- 1928–1938: 4 provinces: Bohemia, Moravia-Silesia, Slovakia and Subcarpathian Ruthenia; divided into districts
- late 1938–March 1939: like above, but Slovakia and Subcarpathian Ruthenia were promoted to "autonomous lands", while the border regions were ceded to Germany (so-called Sudetenland) and Hungary (southern parts of Slovakia and Subcarpathian Ruthenia)
- 1939–1945: Bohemia and Moravia became the protectorate Germany, the remainder of Subcarpathian Ruthenia annexed by Hungary, while Slovakia was nominally independent
- 1945–1948: like 1928–1938, except that Subcarpathian Ruthenia became part of the Soviet Union in 1945
- 1949–1960: 19 regions divided in 270 districts; Czech historical provinces/lands abolished
- 1960–1992: see above