Albula/Alvra
Albula/Alvra is a municipality in the Albula Region in the canton of Graubünden in Switzerland. On 1 January 2015 the former municipalities of Alvaschein, Mon, Stierva, Tiefencastel, Alvaneu, Brienz/Brinzauls and Surava merged to form the new municipality of Albula/Alvra.[3]
Albula/Alvra | |
|---|---|
 Mon village from the air | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Albula/Alvra 
| |
 Albula/Alvra  Albula/Alvra | |
| Coordinates: 46°38′N 9°33′E | |
| Country | Switzerland |
| Canton | Graubünden |
| District | Albula |
| Area | |
| • Total | 93.93 km2 (36.27 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 1,231 m (4,039 ft) |
| Population (2018-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 1,310 |
| • Density | 14/km2 (36/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (Central European Time) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (Central European Summer Time) |
| Postal code(s) | 7084,7450,51,58,59,72,92 |
| SFOS number | 3542 |
| Surrounded by | Riom-Parsonz, Salouf |
| Website | www SFSO statistics |
History
Alvaschein
The first mention of the municipality came in 1154, on the occasion of the construction of nunnery named Alvasinis.[4] It became subordinate to the Princes-Bishop of Chur in 1282. In 1367 it belonged to the municipality of Gotteshausband. The inhabitants finally bought their freedom from the Princes-Bishop in 1732. Nearly the whole community was destroyed in a fire in 1745. It has been the seat of the district of the same name since 1851.
Mon
Mon is first mentioned around 1001-1200 as de Maune. In 1281 it was mentioned as Mans.[5] Until 1943 Mon was known as Mons.[6]
Tiefencastel
Tiefencastel is first mentioned in 831 as in Castello Impitinis. Starting around in the 14th Century it was known as Tüffenkasten.[8]
Alvaneu
Alvaneu is first mentioned in 1244 as Aluenude. In 1530 it was mentioned as Allweneü.[9] On 20 March 2007 Peter Martin Wettler, a media expert and resident of Zurich was appointed Prince of Belfort by the village's authorities. He was to serve for one year with a mandate to improve tourism and the local economy.[10]
Brienz/Brinzauls
Brienz/Brinzauls is first mentioned around 840 as Brienzola.[11]
By the 12th century the village was an economic center for the Bishop of Chur. The Lords of Brienz were first mentioned as the owners of a fortified tower in the village in 1259. The tower fell in ruin and was demolished in 1880. Until 1851, the village was part of the Herrschaft of Belfort. Between 1869 and 1883 Brienz/Brinzauls and Surava were united into a single political municipality. In 1874, a fire damaged or destroyed much of the village.[11]
The village church was first mentioned in 840. In 1519 St. Calixtus became the patron saint of this church. In 1526 it separated from the parish of Lantsch/Lenz to become a parish. In 1725 Surava separated from Brienz/Brinzauls to form its own parish.[11]
In 1870-73 the Landwasserstrasse was built which helped connect the village to the rest of the country. Beginning in the 1960s the number of local farmers began to drop, however agriculture still remains important. In 1990, about 43% of all jobs in the municipality were in agriculture. In 1860 the entire population spoke Romansh. By 1990 it had dropped to only 58%.[11]
Surava
Surava is first mentioned about 1580 as Surraguas.[12]
Geography

Based on the 2009 survey, the former municipalities that make up Albula/Alvra had an area of 93.93 km2 (36.27 sq mi).[13] Of this area, 26.37 km2 (10.18 sq mi) or 28.1% was used for agricultural purposes, while 43.53 km2 (16.81 sq mi) or 46.3% was forested. Of the rest of the land, 2.62 km2 (1.01 sq mi) or 2.8% was settled (buildings or roads), 0.99 km2 (0.38 sq mi) or 1.1% was either rivers or lakes and 20.46 km2 (7.90 sq mi) or 21.8% was unproductive land.[14]
Of the built up area, housing and buildings made up 0.9% and transportation infrastructure made up 1.3%. Out of the forested land, 41.3% of the total land area is heavily forested and 2.1% is covered with orchards or small clusters of trees. Of the agricultural land, 1.0% is used for growing crops and 8.6% is pastures and 18.5% is used for alpine pastures. Of the water in the municipality, 0.2% is in lakes and 0.8% is in rivers and streams. Of the unproductive areas, 6.4% is unproductive vegetation and 15.4% is too rocky for vegetation.[14]
Demographics
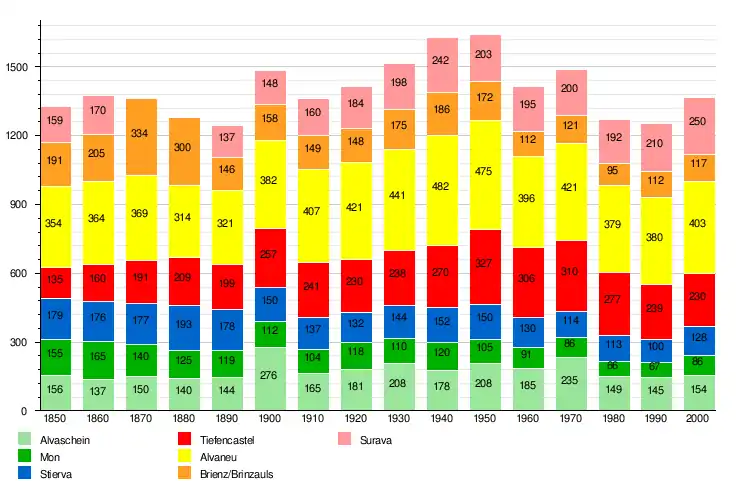
The total population of Albula/Alvra (as of December 2019) is 1,283.[15]
Climate
Tiefencastel has an average of 98.6 days of rain per year and on average receives 784 mm (30.9 in) of precipitation. The wettest month is August during which time Tiefencastel receives an average of 110 mm (4.3 in) of precipitation. During this month there is precipitation for an average of 10.8 days. The month with the most days of precipitation is June, with an average of 11.3, but with only 92 mm (3.6 in) of precipitation. The driest month of the year is February with an average of 35 mm (1.4 in) of precipitation over 10.8 days.[17]
Heritage sites of national significance
Parts of the UNESCO World Heritage Site, the Rhaetian Railway in the Albula / Bernina Landscapes run through the municipality. The Carolingian-era church of St. Peter Mistail in Alvaschein, the baroque Church of St. Franziskus/S. Francestg in Mon and the parish church of St. Stefan/S. Stefan in Tiefencastel are listed as Swiss heritage sites of national significance. The village of Alvaschein is part of the Inventory of Swiss Heritage Sites.[18]
The Capuchin built church of St. Franziskus/S. Francestg dates from 1643-48. The frescoes were finished by Johann Rudolf Sturn, but in 1915 were partially painted over. However, following the renovation in 1975, the original frescoes are once again visible.[5]
The church of St. Stefan/S. Stefan was first mentioned in 1343. In 1650 it was rebuilt and expanded by the Capuchin monks. During this renovation it was given extensive wood carvings and paintings.

 Church of S. Peder E Conturn or St. Peter Mistail in Alvaschein
Church of S. Peder E Conturn or St. Peter Mistail in Alvaschein Church of St. Franziskus/S. Francestg in Mon
Church of St. Franziskus/S. Francestg in Mon Parish church of St. Stefan/S. Stefan in Tiefencastel
Parish church of St. Stefan/S. Stefan in Tiefencastel
References
- "Arealstatistik Standard - Gemeinden nach 4 Hauptbereichen". Federal Statistical Office. Retrieved 13 January 2019.
- "Ständige Wohnbevölkerung nach Staatsangehörigkeitskategorie Geschlecht und Gemeinde; Provisorische Jahresergebnisse; 2018". Federal Statistical Office. 9 April 2019. Retrieved 11 April 2019.
- Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz published by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office (in German) accessed 2 January 2013
- Alvaschein in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Mon in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz published by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office (in German) accessed 23 September 2009
- Stierva in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Tiefencastel in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Alvaneu in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Leybold-Johnson, Isobel (March 20, 2007). "Mountain village converts to a princedom". Swissinfo. Retrieved 24 September 2009.
- Brienz/Brinzauls in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Surava in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Arealstatistik Standard - Gemeindedaten nach 4 Hauptbereichen
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics 2009 data (in German) accessed 15 January 2015
- "Ständige und nichtständige Wohnbevölkerung nach institutionellen Gliederungen, Geburtsort und Staatsangehörigkeit". bfs.admin.ch (in German). Swiss Federal Statistical Office - STAT-TAB. 31 December 2019. Retrieved 6 October 2020.
- Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB Bevölkerungsentwicklung nach Region, 1850-2000 Archived 2012-03-17 at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 29 January 2011
- "Temperature and Precipitation Average Values-Table, 1961-1990" (in German, French, and Italian). Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology - MeteoSwiss. Archived from the original on 27 June 2009. Retrieved 8 May 2009., the weather station elevation is 885 meters above sea level.
- Swiss inventory of cultural property of national and regional significance Archived 2009-05-01 at the Wayback Machine 21.11.2008 version, (in German) accessed 25-Sep-2009
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Albula/Alvra. |
- Alvaschein in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Mon in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Alvaneu in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Surava in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Gemeinde Alvaneu—official site of Alvaneu (in German)
- Bad Alvaneu—Alvaneu thermal baths (in German)
- Surava Official website (in German)