Aspergillus halophilicus
Aspergillus halophilicus is a species of fungus in the genus Aspergillus. It is from the Robusti section.[2] The species was first described in 1959.[1] It has been isolated from dried corn in the United States and a textile in the Netherlands.[2] It has been reported to produce chaetoviridin A, deoxybrevianamid E, pseurotin A, pseurotin D, rugulusovin, stachybotryamide, and tryprostatin B.[2]
| Aspergillus halophilicus | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Eurotiomycetes |
| Order: | Eurotiales |
| Family: | Trichocomaceae |
| Genus: | Aspergillus |
| Species: | A. halophilicus |
| Binomial name | |
| Aspergillus halophilicus C.M. Christensen, Papavizas & C.R. Benjamin (1959)[1] | |
Growth and morphology
A. halophilicus has been cultivated on both Czapek yeast extract agar (CYA) plates and yeast extract sucrose agar (YES) plates. The growth morphology of the colonies can be seen in the pictures below.
 Aspergillus halophilicus growing on CYA plate
Aspergillus halophilicus growing on CYA plate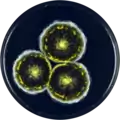 Aspergillus halophilicus growing on YES plate
Aspergillus halophilicus growing on YES plate
References
- Christensen, C.M.; Papavizas, G.C.; Benjamin, C.R. 1959. A new halophilic species of Eurotium. Mycologia. 51(5):636-640
- Sklenar, F.; Jurjevic, Z.; Zalar, P.; Frisvad, J.C.; Visagie, C.M.; Kolarik, M.; Houbraken, J.; Chen, A.J.; Yilmaz, N.; Seifert, K.A.; Coton, M.; Déniel, F.; Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Samson, R.A.; Peterson, S.W.; Hubka, V. (2017). "Phylogeny of xerophilic aspergilli (subgenus Aspergillus) and taxonomic revision of section Restricti". Studies in Mycology. 88: 161–236. doi:10.1016/j.simyco.2017.09.002. PMC 5678892.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.