Aspergillus olivicola
Aspergillus olivicola is a species of fungus in the genus Aspergillus. It is from the Nidulantes section.[2] The species was first described in 2008.[1] It has been isolated from fruit in Italy. A. olivicola has been shown to produce aflatoxin B1, emericellin, shamixanthone, siderin, sterigmatocystin, terrain, and varitriol.[3]
| Aspergillus olivicola | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Eurotiomycetes |
| Order: | Eurotiales |
| Family: | Trichocomaceae |
| Genus: | Aspergillus |
| Species: | A. olivicola |
| Binomial name | |
| Aspergillus olivicola Frisvad, Zalar & Samson (2008)[1] | |
In 2016, the genome of A. olivicola was sequenced as a part of the Aspergillus whole-genome sequencing project - a project dedicated to performing whole-genome sequencing of all members of the genus Aspergillus.[4] The genome assembly size was 33.17 Mbp.[4]
Growth and morphology
Aspergillus olivicola has been cultivated on both Czapek yeast extract agar (CYA) plates and Malt Extract Agar Oxoid® (MEAOX) plates. The growth morphology of the colonies can be seen in the pictures below.
 Aspergillus olivicola growing on CYA plate
Aspergillus olivicola growing on CYA plate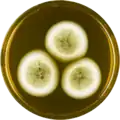 Aspergillus olivicola growing on MEAOX plate
Aspergillus olivicola growing on MEAOX plate
References
- Zalar, P.; Frisvad, J.C.; Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Varga, J.; Samson, R.A. 2008. Four new species of Emericella from the Mediterranean region of Europe. Mycologia. 100(5):779-795
- Chen, A.J.; Frisvad, J.C.; Sun, B.D.; Varga, S.; Kocsubé, S.; Dijksterhuis, J.; Kim, D.H.; Hong, S.-B.; Houbraken, J.; Samson, R.A. (2016). "Aspergillus section Nidulantes (formerly Emericella): Polyphasic taxonomy, chemistry and biology". Studies in Mycology. 84: 1–118. doi:10.1016/j.simyco.2016.10.001. PMC 5198626. PMID 28050053.
- Zalar P, Frisvad JC, Gunde-Cimerman N, et al. (2008). Four new species of Emericella from the Mediterranean region of Europe. Mycologia 100: 779 – 795.
- https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/Aspoli1_1/Aspoli1_1.home.html