Atriplex holocarpa
Atriplex holocarpa is a low-growing species of Atriplex (saltbush) found throughout arid regions of Australia.[1] A. holocarpa is commonly known as pop saltbush, because its carpals pop when stepped upon.[2]
| Atriplex holocarpa | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Amaranthaceae |
| Genus: | Atriplex |
| Species: | A. holocarpa |
| Binomial name | |
| Atriplex holocarpa | |
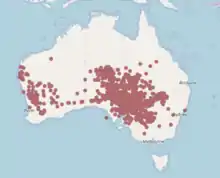 | |
| Atriplex holocarpa range, Atlas of Living Australia | |
Atriplex holocarpa was described by Ferdinand von Mueller during his 1859 voyages through inland Australia.[3] The name 'Atriplex' is from the Latin atriplexum, meaning 'orache', a plant used in ancient times as spinach substitute [4]
The Latin holocarpa describes the spongey carpel and holocarpa denotes the plant's whole (holo-) carpel (-carpa). Atriplex species are typified by seeds enclosed in hard or spongey bodies consisting of two small bracts.[2][1]
Description
Atriplex holocarpa is a small, short-lived forb measuring between 10 and 30 cm.[1][2] A. holocarpa has small, broadly ovate silvery green leaves irregularly notched margins.[1] The leaves turn purplish on maturity.[5]
Atriplex holocarpa is monoecious with small separate male and female flowers on the same plant.[5] The male flowers are found in small clusters in the upper axils and the female flowers are in the lower axils. The fruits are globular pear shaped, from greenish-white through to reddish in colour.[2] The fruits are membranous with net-veined or crinkled and between 6 and 12 mm long[2] A. holocarpa and A. spongiosa are often found growing together.[6] A. holocarpa is differentiated from A. spongiosa in that A. spongiosa has smaller fruiting bodies (4-6mm long) and none or very short leaf stalks while A. holocarpa's fruiting bodies are 4-12mm long and the leaves have conspicuous stalks.[7]
Taxonomy
Atriplex holocarpa is one of approximately 300 Atriplex species,[8] 61 of which are found in Australia.[4] Atriplex species are part of the subfamily Chenopodioideae of the family Amaranthaceae.
Range and habitat
Atriplex holocarpa is an Australian saltbush species[9] found in all states except Tasmania.[10] A. holocarpa is found in arid inland areas of southwestern Queensland, western New South Wales, and northwestern Victoria through to southern Western Australia, often on floodplains or sandy flats. [11] "A. holocarpa" is a halophyte and is very tolerant of saline conditions. They survive in saline drainages and saline rocky hills, but never on sand. A. holocarpa can be sown on saline tailings dams and saline waste dump slopes.[5] Dry temperate flora was already established in Australia 60-70 million years ago when Australia was still connected to the Antarctic southern continent,[12] and ancient elements of arid flora include the halophyte saltbushes of Chenopodiaceae including Atriplex spp. that have no close relatives in wetter parts of the country.[13] A. holocarpa germinates readily in pits created by foraging desert animals such as bilbies, echidnas, bettongs and goannas, as well introduced burrowing animals.[14]
Ecology
Atriplex holocarpa lives in arid, temperate parts of Australia. Emus eat leaves of the plant in summer months[15] but in the main most animals find A. holocarpa unpalatable and only eat it when forced.[5] The presence of this little forb is indicative of poor rangeland conditions[5] with A. holocarpa numbers increasing as grazing pressure increases.[16] due to their general unpalatability.[5]
After setting seed, the seedcase of A. holocarpa develops a lemon-shaped or globular spongy mass around the seed. At maturity the seed cases turn blackish and fall to the ground[5] A. holocarpa is very tolerant of saline conditions and can be used to help colonise saline waste dumps.[5] Salts are extruded through the plants' vesiculated hairs to prevent salt reaching toxic levels.[17] A. holocarpa have unicellular salt bladders on both surfaces of their leaves that concentrate salt above the saturation point of NaCl and release to the exterior via the vesiculated hairs.[18]
References
- Moore, P (2005). A guide to plants of inland Australia. Reed New Holland, ISBN 1 876334 86 X
- Cunningham, G. M., Mulhorne, W. E., Milthorpe, P. L., Leigh and J. H. (1992). Plants of Western New South Wales, Inkata Press : Melbourne and Sydney.
- Mueller, F (1859). Report on the plants collected during Mr. Babbage's expedition into the northwestern interior of South Australia in 1858.
- Australian National Herbarium, Atriplex nummularia, https://www.anbg.gov.au/gnp/interns-2007/atriplex-nummularia.html
- Mitchell, A. A. and Wilcox, D.G. (1988) Arid Shrubland Plants of Western Australia, University of Western Australia Press, 2nd ed
- Commonwealth of Australia. (1984). Flora of Australia. Bureau of Flora and Fauna, Canberra, Australian Government Publishing Service.
- plantnet.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au
- Flores, H & Davis, J. I. (2001). A cladistic analysis of atripliceae (Chenopodiaceae) based on morphological data. Journal of Torrey Botanical Society, vol. 128, iss 3.
- Kadereit, G., Mavrodiev, E. V., Zacharias, E. H. and Sukhorukov, A. P. (2010). Molecular phylogeny of Atripliceae (Chenopodioideae, Chenopodiaceae): Implications for systematics, biogeography, flower and fruit evolution, and the origin of C4 photosynthesis. American Journal of Botany, vol. 97, iss. 10: 1664-1687
- Commonwealth of Australia. (1984). Flora of Australia. Bureau of Flora and Fauna, Canberra, Australian Government Publishing Service.
- https://bie.ala.org.au/species/http://id.biodiversity.org.au/node/apni/2919449
- Carolin, R. C. (1982) A review and critique of studies on the phytogeography of arid Australia, in Barker, W. R and Greenslade, P.J.M. (1982) . Evolution of the flora and fauna of arid Australia, Peacock Publication : Frewville South Australia
- Keith, D. A. (2004). Ocean Shores to Desert Dunes: The natural vegetation of New South Wales and the ACT, New South Wales National Parks and Wildlife Service & Department of Infrastructure, Planning and Natural Resources.
- James, A. I., Eldridge, D. J., Hill, B. M.. (2009). Foraging animals create fertile patches in an Australalian desert scrubland. Ecography, vol. 32.
- Dunstan, H., Florentine, S. K., Calviño-Cancela, M., Westbrooke, M. E & Palmer, G. C.(2013). Dietary characteristics of Emus (Dromaius novaehollandiae) in semi-arid New South Wales, Australia, and dispersal and germination of ingested seeds, Austral Ornithology, 113:2
- Waudby, H. P. and Petit. S.(2015). Ephemeral plant indicators of livestock grazing in arid rangelands during wet conditions.The Rangeland Journal, CSIRO Publishing, 37, 323–33.0
- Mozafar, A. and Goodin, l.R. 1970. Vesiculated hairs: a mechanism for salt tolerance in Atriplex halimus L. Plant Physiology 45: 62-65.
- Rajput, P. and Sen, D. N. (1991). Annals of Arid Zone, vol 30. iss. 4.