Barium carbide
Barium carbide (also referred to as Barium ethynediide or Barium acetylide)[1] is a chemical compound in the carbide family with the chemical formula C2Ba.[2]
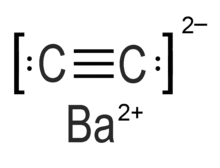 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Barium ethynediide | |
| Other names
Barium acetylide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| BaC2 | |
| Molar mass | 161.35 g/mol |
| Appearance | black crystalline solid |
| Density | 3.75 g/cm3 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Preparation
Barium carbide was first synthesized as an impure compound in the Soviet Union in 1986 by reducing Barium carbonate powder with metallic Magnesium in the presence of Carbon-14.[3] It can also be prepared by heating a Barium amalgam and Carbon powder mixture in a Hydrogen current. The pure compound is prepared by reducing Barium oxide with Carbon at a high temperature.[4]
Properties
Barium carbide reacts similarly to Calcium carbide,[5] but it's more fusible. When exposed to extreme heat, the Barium will evaporate leaving behind crystals of Graphite. It can also absorb the Carbon in a solution at high temperatures.[4]
References
- "Barium acetylide | C2Ba | ChemSpider". www.chemspider.com. Retrieved 2019-12-17.
- Elements, American. "Barium Carbide". American Elements. Retrieved 2019-12-11.
- Mishin, V. I.; Georgievskij, S. S.; Eksel', L. M.; Koval', A. I.; Afanas'eva, L. A.; Puchkov, L. D.; Ulybin, V. B. (1989-12-07). "Method for preparation of barium carbide labelled by carbon 14" (in Russian). Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Barium Carbide, BaC2". barium.atomistry.com. Retrieved 2019-12-11.
- "carbide". InfoPlease. Retrieved 2019-12-11.