Barstar
Barstar is a small protein synthesized by the bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Its function is to inhibit the ribonuclease activity of its binding partner barnase, with which it forms an extraordinarily tightly bound complex within the cell until barnase is secreted.[2][3] Expression of barstar is necessary to counter the lethal effect of expressed active barnase. The structure of the barnase-barstar complex is known.[4]
| Barstar (barnase inhibitor) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
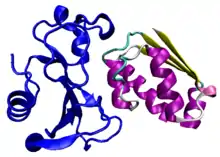 | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | Barstar | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF01337 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000468 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1brs / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
References
- PDB: 1BRS; Buckle AM, Schreiber G, Fersht AR (August 1994). "Protein-protein recognition: crystal structural analysis of a barnase-barstar complex at 2.0-A resolution". Biochemistry. 33 (30): 8878–89. doi:10.1021/bi00196a004. PMID 8043575.
- Hartley RW (1989). "Barnase and barstar: two small proteins to fold and fit together". Trends Biochem. Sci. 14 (11): 450–454. doi:10.1016/0968-0004(89)90104-7. PMID 2696173.
- Hartley RW (1988). "Barnase and barstar. Expression of its cloned inhibitor permits expression of a cloned ribonuclease". J. Mol. Biol. 202 (4): 913–915. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(88)90568-2. PMID 3050134.
- Fersht AR, Buckle AM, Schreiber G (1994). "Protein-protein recognition: crystal structural analysis of a barnase-barstar complex at 2.0-A resolution". Biochemistry. 33 (30): 8878–8889. doi:10.1021/bi00196a004. PMID 8043575.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.