Battery simulator
The battery simulator is a simple and flexible electronic device, designed to test battery chargers of any voltage and power quickly and easily. Simulating the behavior of a battery during the charging process.

History
A battery simulator has the purpose to check that the battery charger works properly so that the battery charge is effective. The proper maintenance of the batteries helps to optimize their life cycle, with the charger being the team in charge of recharging the battery until the energy extracted is completely recovered. So checking that the charging operation is carried out properly means that the battery is charged faster and that it takes more time to discharge
The battery simulator eliminates the need to connect a battery to the charger to be able to test it and allows to know the state of the battery to perform a better maintenance and the necessary repairs, optimizing the daily capacity and the useful life of the battery.
Uses
A Battery simulator has these uses:
- Test battery chargers (current or voltage of any kind) eliminating the need to connect a battery to the charger to test it; simulates the behavior of a battery during the charging process and allows the technician the ability to perform complete tests quickly, safely and accurately any charger.
- To thoroughly test battery chargers quickly without actually waiting for the battery to charged or discharged.[1]
- To test a battery-powered systems by replacing the real battery with a simulator.
- To simulate the battery’s state-of-charge as the battery is being charged or discharged.
Characteristics
Highlights in the battery simulator are the IGBT or MOSFET high frequency regulator (which allows the equipment to work with constant current and voltage), the programmable digital panel.
On the front panel of the equipment there may be the following elements:
- Digital voltmeter
- Analogue ammeter
- Test voltage selector
- Potentiometer fine tension adjustment.
- Potentiometer current selection (0-200 A)
- self-test
- automatic stop in case of failure.
- It has thermal protection of all electronic components and the resistance bank in case of overtemperature (for example: if there are problems in the fans or air ducts clogged the equipment goes to stand-by mode).
Functioning
Battery simulator mimics a battery’s electrical characteristic of outputting a voltage and able to source as well as sink current.[2] A battery simulator is a special kind of power supply that can output positive voltage while can sink and source current. This type of power supply is called two-quadrant power supply. In contrast, a conventional power supply can only source current when the voltage is positive.
Battery simulator able to set the simulated battery voltage either remotely via PC or manually. Often battery simulator has built-in voltage and current display and monitoring. For example the user selects the voltage of the battery to be simulated, using the potentiometer (knob) for adjusting the voltage, while the current value is displayed on the digital screen. An independent potentiometer is available to select the maximum current that the equipment can source or sink.[3]
Battery Charger Testing
The basic use of battery simulator is replacing a real battery with a simulator. This is enables the testing of the charger quickly both at the bench during development stage and production testing at mass production stage. The simulator can change the emulated battery voltage at the touch of button or the turn of knob. If a real battery is used, it will take much longer for the battery voltage to change. For example, a battery simulator can easily adjust its voltage over the range of 0V to 4.2V to test a lithium-ion battery charger. Battery simulator is powerful and convenient tool for testing battery chargers.
Once the simulated battery voltage is set, the user connects the charger to be tested to the input of the simulator. The charger will detect that a battery has been connected and the charging process will begin. The simulator keeps the voltage constant at the set value, while the analogue ammeter indicates the charging current. If the battery simulator has current limit feature and if the current exceed the maximum set value, the simulator automatically increases the voltage to limit the current[4]
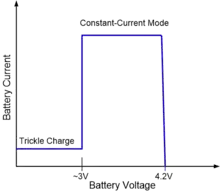
The advantage a battery simulator is its ability to freely set the emulated battery voltage to any value in order to test the charger. For example, a real charger profile curved is obtained by sweeping the simulator voltage while recording its voltage and current. The figure to the right shows a typical Lithium ion charging profile curve obtained by using a battery simulator. The profile curve of the charger is obtained in a few minutes.[5]
Input Power
Battery simulator AC input voltage requirement is typically universal voltage (85-135 or 180-250 VAC), and the frequency is 50 or 60 Hz.
References
- "Battery Simulator Provides Mobile Insurance". Power Electronics. 2016-01-22. Retrieved 2018-06-09.
- "Battery Simulator". www.accelinstruments.com. Retrieved 2018-06-09.
- DATTA, ABHIK. "Design of a Lead Acid Battery Charger System" (PDF).
- Uddin, Ahmed. "DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF LITHIUMION BATTERY THERMAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEM FOR MILD HYBRID VEHICLE APPLICATION" (PDF). SAE International.
- Ramadesigan, Venkatasailanathan; Northrop, Paul W. C.; De, Sumitava; Santhanagopalan, Shriram; Braatz, Richard D.; Subramanian, Venkat R. (2012). "Modeling and Simulation of Lithium-Ion Batteries from a Systems Engineering Perspective" (PDF). Journal of the Electrochemical Society. 159 (3): R31–R45. doi:10.1149/2.018203jes.