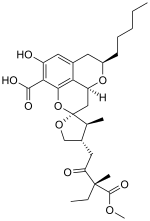
Berkelic acid
Berkelic acid is a fungal isolate with anticancer activity in vitro.[1] It was first discovered in the fungal species Euglena Mutabilis, which evolved to live in the Berkeley Pit.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C29H40O9 | |
| Molar mass | 532.6 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Notes
- Stierle, AA; Stierle, DB; Kelly, K (2006). "Berkelic acid, a novel spiroketal with selective anticancer activity from an acid mine waste fungal extremophile". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 71 (14): 5357–60. doi:10.1021/jo060018d. PMID 16808526.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.