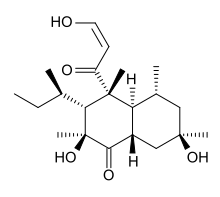
Betaenone C
Betaenone C, like other betaenones (A and B), is a secondary metabolite isolated from the fungus Pleospora betae, a plant pathogen.[1] Of the seven phytotoxins isolated in fungal leaf spots from sugar beet (Beta vulgaris), it showed 89% growth inhibition. Betaenone C has been shown to act by inhibiting RNA and protein synthesis.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S,3R,4R,4aS,5R,7R,8aS)-3-[(2R)-butan-2-yl]-2,7-dihydroxy-4-[(2Z)-3-hydroxyprop-2-enoyl]-2,4,5,7-tetramethyloctahydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H34O5 | |
| Molar mass | 366.498 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Ichihara A.; Oikawa, Hideaki; Hayashi, Kazuko; Sakamura, Sadao; Furusaki, Akio; Matsumoto, Takeshi (1983). "Structures of Betaenones A and B, Novel Phytotoxins from Phoma betae Fr". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 105: 2907–2908. doi:10.1021/ja00347a070.
- Haraguchi, T.; Oguro, Mieko; Nagano, Hiroshi; Ichihara, Akitami; Sakamura, Sadao (1983). "Specific inhibitors of eukaryotic DNA synthesis and DNA polymerase α, 3-deoxyaphidicolin and aphidicolin-17-monoacetate". Nucleic Acids Res. 11: 1197–2000. doi:10.1093/nar/11.4.1197. PMC 325786.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.