Bilobol
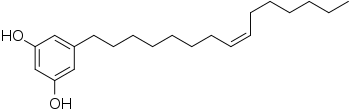
Bilobol is an alkylresorcinol, a type of phenolic lipids composed of long aliphatic chains and phenolic rings. Chemically, it is similar in structure to urushiol, the irritant found in poison ivy; it is a strong skin irritant itself.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5-[(Z)-Pentadec-8-enyl]benzene-1,3-diol | |
| Other names
5-[(Z)-Pentadec-8-enylo]resorcinol 5-Pentadecenylresorcinol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H34O2 | |
| Molar mass | 318.501 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Natural occurrences
Bilobol can be found in Ginkgo biloba fruits.[2]
References
- Matsumoto, Kazuyuk i; Fujimoto, Masao; Ito, Kazuo; Tanaka, Hitoshi; Hirono, Iwao (1990). "Comparison of the effects of bilobol and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate on skin, and test of tumor promoting potential of bilobol in CD-1 mice". The Journal of Toxicological Sciences. 15 (1): 39–46. doi:10.2131/jts.15.39. PMID 2110595.
- Tanaka, A; Arai, Y; Kim, SN; Ham, J; Usuki, T (2011). "Synthesis and biological evaluation of bilobol and adipostatin A". Journal of Asian Natural Products Research. 13 (4): 290–6. doi:10.1080/10286020.2011.554828. PMID 21462031. S2CID 25305504.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.