CBX2 (gene)
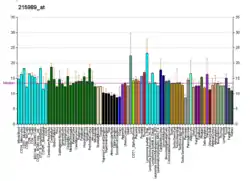
Chromobox protein homolog 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CBX2 gene.[5][6][7] According to a New Scientist article CBX2 controls human sex even more so than X/Y chromosomes.[8]
Interactions
CBX2 (gene) has been shown to interact with RYBP.[9] It also interacts with the testis determining factor encoded by the SRY gene on the Y chromosome, as both proteins are necessary components of the male cascade.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000173894 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000025577 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Gecz J, Gaunt SJ, Passage E, Burton RD, Cudrey C, Pearce JJ, Fontes M (Jul 1995). "Assignment of a Polycomb-like chromobox gene (CBX2) to human chromosome 17q25". Genomics. 26 (1): 130–3. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(95)80091-Y. PMID 7782071.
- Chodak GW (Nov 1989). "Early detection and screening for prostatic cancer". Urology. 34 (4 Suppl): 10–2, discussion 46–56. doi:10.1016/0090-4295(89)90228-8. PMID 2477932.
- "Entrez Gene: CBX2 chromobox homolog 2 (Pc class homolog, Drosophila)".
- Ewen Callaway. "Girl with Y chromosome sheds light on maleness ", New Scientist, 2009-04-09. Retrieved on 2009-04-14.
- García E, Marcos-Gutiérrez C, del Mar Lorente M, Moreno JC, Vidal M (Jun 1999). "RYBP, a new repressor protein that interacts with components of the mammalian Polycomb complex, and with the transcription factor YY1". EMBO J. 18 (12): 3404–18. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.12.3404. PMC 1171420. PMID 10369680.
External links
- Human CBX2 genome location and CBX2 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Brandenberger R, Wei H, Zhang S, Lei S, Murage J, Fisk GJ, Li Y, Xu C, Fang R, Guegler K, Rao MS, Mandalam R, Lebkowski J, Stanton LW (2004). "Transcriptome characterization elucidates signaling networks that control human ES cell growth and differentiation". Nat. Biotechnol. 22 (6): 707–16. doi:10.1038/nbt971. PMID 15146197. S2CID 27764390.
- García E, Marcos-Gutiérrez C, del Mar Lorente M, Moreno JC, Vidal M (1999). "RYBP, a new repressor protein that interacts with components of the mammalian Polycomb complex, and with the transcription factor YY1". EMBO J. 18 (12): 3404–18. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.12.3404. PMC 1171420. PMID 10369680.
- Katoh-Fukui Y, Tsuchiya R, Shiroishi T, Nakahara Y, Hashimoto N, Noguchi K, Higashinakagawa T (1998). "Male-to-female sex reversal in M33 mutant mice". Nature. 393 (6686): 688–92. doi:10.1038/31482. PMID 9641679. S2CID 4399183.
- Pearce JJ, Singh PB, Gaunt SJ (1992). "The mouse has a Polycomb-like chromobox gene". Development. 114 (4): 921–9. PMID 1352241.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.