Carte de l'Égypte (Description de l'Égypte)
The Carte de l'Égypte (English: Map of Egypt), from the Description de l'Égypte, was the first triangulation-based map of Egypt, Syria and Palestine. The mapmaking expedition was led by Pierre Jacotin. It was used as the basis for many most maps of the region for much of the nineteenth century.[1][2]
.png.webp)
Jacotin's 1799 survey of Egypt and Palestine, as a composite, published in 1818 (Carte geographique de l'Egypte et des pays environnans. Reduite d'apres la Carte topographique levee pendant l'expedition de l'Armee francaise)
Illustration of the assembly of the 47 sheets
It was originally prepared during the 1799-1800 French campaign in Egypt and Syria. Despite the maps being dated 1818 and 1826, they were not published until 1828–30.[3]
The maps can be seen in detail at Wikimedia Commons: Carte topographique de l’Égypte.
Editions and related documents
- First edition: Cartes géographiques et topographiques. Paris. 1818. p. 53.
- Second edition: C.L.F. Panckoucke, ed. (1826). Atlas géographique. Paris. p. 57.
- Memoir: Mémoire sur la construction de la carte de l'Egypte par M. Jacotin
- Supplementary tables: Jacotin, M.: Tableau de la superficie de l'Égypte
- Baring, Sir Thomas (1838). "Cartes Géographiques Et Topographiques". A Bibliographical Account And Collation Of La Description De L'Égypte: Presented To The Library Of The London Institution, By Sir Thomas Baring, Baronet, President: With A List Of The Other Donations Made To That Establishment From April 1837 To April 1838. London Institution.
Maps of Palestine - Files 43-47
.jpg.webp) 43: Gaza
43: Gaza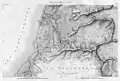 44: Jerusalem and Jaffa
44: Jerusalem and Jaffa 45: Cesearea
45: Cesearea 46: Acre
46: Acre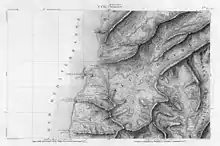 47: Tyre
47: Tyre
See also
Bibliography
- Khatib, Hisham (2003). Palestine and Egypt Under the Ottomans: Paintings, Books, Photographs, Maps and Manuscripts. I. B. Tauris. ISBN 1-860-64888-6.
- Kallner, D. H. (1944). "Jacotin's Map of Palestine". Quarterly Statement - Palestine Exploration Fund. 76: 157–163. doi:10.1179/peq.1944.76.1.157.
- Schelhaas, Bruno; Faehndrich, Jutta; Goren, Haim (28 February 2017). Mapping the Holy Land: The Foundation of a Scientific Cartography of Palestine. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-0-85772-785-5.
- Karmon, Yehuda (1960a). "An Analysis of Jacotin's Map of Palestine". Israel Exploration Journal. 10 (3): 155–173. JSTOR 27924824.
- Karmon, Yehuda (1960b). "An Analysis of Jacotin's Map of Palestine". Israel Exploration Journal. 10 (4): 244–253. JSTOR 27924833.
References
- Karmon 1960a, p. 155.
- Schelhaas, Faehndrich & Goren 2017, p. 66.
- Khatib, 2003, p. 211
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Carte de l'Égypte (Description de l'Égypte). |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.