Cfr10I/Bse634I
In molecular biology, the Cfr10I/Bse634I family of restriction endonucleases includes the type II restriction endonucleases Cfr10I and Bse634I. They exhibit a conserved tetrameric architecture that is of functional importance, wherein two dimers are arranged, back-to-back, with their putative DNA-binding clefts facing opposite directions. These clefts are formed between two monomers that interact, mainly via hydrophobic interactions supported by a few hydrogen bonds, to form a U-shaped dimer. Each monomer is folded to form a compact alpha-beta structure, whose core is made up of a five-stranded mixed beta-sheet. The monomer may be split into separate N-terminal and C-terminal subdomains at a hinge located in helix alpha3.[1] Both Cfr10I and Bse634I recognise the double-stranded sequence RCCGGY and cleave after the purine R.[2]
Recognition sequence Cut 5' RCCGGY 5' ---R CCGGY--- 3' 3' YGGCCR 3' ---YGGCC R--- 5'
| Bse634I | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
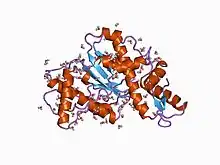 crystal structure of citrobacter freundii restriction endonuclease cfr10i at 2.15 angstroms resolution. | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Bse634I | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF07832 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR012415 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
References
- Grazulis S, Deibert M, Rimseliene R, Skirgaila R, Sasnauskas G, Lagunavicius A, Repin V, Urbanke C, Huber R, Siksnys V (February 2002). "Crystal structure of the Bse634I restriction endonuclease: comparison of two enzymes recognizing the same DNA sequence". Nucleic Acids Res. 30 (4): 876–85. doi:10.1093/nar/30.4.876. PMC 100338. PMID 11842098.
- Bozic D, Grazulis S, Siksnys V, Huber R (January 1996). "Crystal structure of Citrobacter freundii restriction endonuclease Cfr10I at 2.15 A resolution". J. Mol. Biol. 255 (1): 176–86. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0015. PMID 8568865.