Cobamide
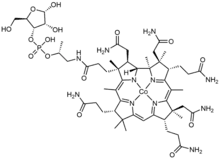
Cobamide is a naturally occurring chemical compound containing cobalt in the corrinoid family of macrocyclic complexes. Cobamide works as a coenzyme with some enzymes in bacteria. The cobalt atom may have a transferable methyl group attached. It is used for example in 5-methyltetrahydrosarcinapterin:corrinoid/iron-sulfur protein Co-methyltransferase.[1][2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
cobalt;[(2R,3S,4R,5S)-4,5-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-3-yl] [(2R)-1-[3-[(1R,2R,3R,4Z,7S,9Z,12S,13S,14Z,17S,18S,19R)-2,13,18-tris(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-7,12,17-tris(3-amino-3-oxopropyl)-3,5,8,8,13,15,18,19-octamethyl-2,7,12,17-tetrahydro-1H-corrin-21-id-3-yl]propanoylamino]propan-2-yl] hydrogen phosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C53H81CoN11O15P | |
| Molar mass | 1202.200 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Maupin-Furlow, J.; Ferry, J.G. (1996). "Characterization of the cdhD and cdhE genes encoding subunits of the corrinoid/iron-sulfur enzyme of the CO dehydrogenase complex from Methanosarcina thermophila". J. Bacteriol. 178 (2): 340–346. PMC 177663. PMID 8550451.
- Grahame, D.A.; DeMoll, E. (1996). "Partial reactions catalyzed by protein components of the acetyl-CoA decarbonylase synthase enzyme complex from Methanosarcina barkeri". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (14): 8352–8358. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.14.8352. PMID 8626532.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.