Congress of Baja California
The Congress of the State of Baja California (Spanish: Congreso del Estado de Baja California) is the legislative branch of the government of the State of Baja California. The Congress is the governmental deliberative body of Baja California, which is equal to, and independent of, the executive.
Congress of the State of Baja California | |
|---|---|
| XXIII Legislature | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Leadership | |
President | Victor Manuel
Moran Hernández, MORENA |
Vice President | María Trinidad
Vaca Chacón |
Secretary | Carmen Leticia
Hernández Carmona, MORENA |
Pro-secretary | Gerardo
López Montes, PRD |
Scrutinizing secretary | Julia Andrea
González Quiroz, MORENA |
| Structure | |
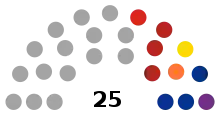
| Seats | 25 |
 | |
Political groups | |
| Authority | Title III, Chapter I, Article 13 of the Political Constitution of the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California |
| Salary | $62,226 MXN[1] |
| Elections | |
| First-past-the-post for 17 electoral district seats and Mixed-member proportional representation for 8 proportional representation seats | |
Last election | June 5, 2016 |
| Meeting place | |
| Mexicali, Baja California, Mexico | |
| Website | |
| www.congresobc.gob.mx | |
The Congress is unicameral and consists of 25 deputies. 17 deputies are elected on a first-past-the-post basis, one for each district in which the entity is divided, while 8 are elected through a system of proportional representation. Deputies are elected to serve for a three-year term.
The Congress convenes in the Legislative Power building (edificio del Poder Legislativo), which is located in Mexicali, the capital city of the State.
Structure
In order to carry out its duties, the Congress is organized in the following manner:
- Management bodies (Órganos de Dirección):
- The Board of Directors;
- The Political Coordination Board (JUCOPO).
- Working bodies (Órganos de Trabajo):
- Legislative Advice Committees;
- Standing Committees.
- Technical and Administrative bodies (Órganos Técnicos y Administrativos):
- Administrative Department;
- Accounting and Finance Department;
- Legislative Consulting Department;
- Auxiliary Departments:
- Legal Affairs Unit;
- Internal Comptroller Unit;
- Transparency Unit;
- Social Communication Unit.
References
- Estado a estado: ¿cuánto ganan los diputados locales? by Ángel Nakamura, accessed 6 July 2018