Coprinopsis lagopus
Coprinopsis lagopus is a species of fungus in the family Psathyrellaceae. Until 2001, the species was known as Coprinus lagopus; advances in the understanding of phylogenetic relationships between the various coprinoid species led to a major reorganization of that genus.[1] It is a delicate and short-lived fungus, the fruit bodies lasting only a few hours before dissolving into a black ink – a process called deliquescence.[2] The vague resemblance of the young fruit body to the paw of a white rabbit has earned this species the common name harefoot mushroom.[3]
| Coprinopsis lagopus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Basidiomycota |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes |
| Order: | Agaricales |
| Family: | Psathyrellaceae |
| Genus: | Coprinopsis |
| Species: | C. lagopus |
| Binomial name | |
| Coprinopsis lagopus (Fr.) Redhead, Vilgalys & Moncalvo (2001) | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
| Coprinopsis lagopus | |
|---|---|
float | |
| gills on hymenium | |
| cap is ovate | |
| hymenium is free | |
| stipe is bare | |
| spore print is black | |
| ecology is saprotrophic | |
| edibility: inedible | |
Description

The fruit body size of Coprinopsis lagopus can vary tremendously. This fungus gives rise to very small fruit bodies (known as dwarf fruit-bodies), some of which are less than one-hundredth the size of the larger ones. In a series of experiments, Arthur Henry Reginald Buller grew spores on horse dung and noted a large range of size variation: the smallest specimen having a stem length of 1 mm and cap diameter of 0.75 mm, while the largest specimen had a stem length of 184 mm and cap diameter of 20 mm.[4] Buller noted that the dwarf fruit-bodies are fully functional, producing and liberating spores in a manner identical with normal ones. The great variation in size has led some authors to erroneously name the dwarf fruit-bodies as new species. For example, George Edward Massee considered the dwarfs to be a new species, Coprinus radiatus.[2] In general, dwarf fruit-bodies have stem lengths from 1–10 mm tall and cap of 0.75–3 mm in diameter, while large specimens have stems that are 130–185 mm tall and cap diameters of 25–40 mm. The thickness of the stem in the larger specimens is typically 4–6 mm thick, up to 0.8 mm thick at the club-shaped or bulbous base.[5]
The color of the cap surface is pale to very dark-brown at center beneath the whitish to silvery grey veil but becomes paler towards the margin. As the mushroom matures, the shape of the cap becomes more conical or convex, and finally flattens out, with edges curved upward. The veil is initially whitish, then turns to a silvery grey or grey-brown; it eventually splits up, becoming hairy (fibrillose). The gills are freely attached to the stem, very thin and crowded closely together. Initially, the color of the gills is white, then progresses to grayish-brown then to black as the spores mature. In maturity the gill edges dissolve (deliquesce) into a black liquid.[6] These mushrooms are evanescent, lasting only last a few hours before death;[7] the autodigestive process is enhanced in humid environments. The stem is whitish in color, and is hollow, hairy (flocculose) over the whole surface but especially at lower part, and becomes smooth (glabrous) with age. The spore print is violet-black.
Microscopic features
Spores have dimensions of 11–13 x 6–8 µm.[7] They are ellipsoid or ovoid in shape, with a rounded base and apex, dark red-brown in color, and nonamyloid.
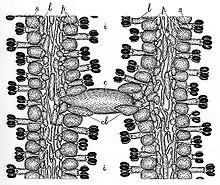
The cystidia found on the sides of the gills (pleurocystidia) are abundant in large fruit bodies, fewer in number in the smaller specimens. These cells are oval, rounded at the apex with a bulge in the middle, and contracted into a stalk at the base. The length of these cells is typically 100–130 µm, with a width of 35–45 µm. Before the cap expands, each cystidium completely branches an interlamellar space, with both ends attached to the gills, help together by clasping paraphyses. As the gill expands the cystidium breaks away from one gill and projects from the other gill. The basidia (spore-bearing cells) comes in two sizes; long basidia have dimensions of 40 × 8–10 µm, while the shorter basidia have dimensions of 23 × 8–10 µm. The basidia have four spores, which are attached by short sterigmata.[8]
Habitat and distribution
Coprinopsis lagopus grows solitarily or in groups on wood chips, compost heaps, vegetable refuse, or horse dung, from autumn to mid-winter. It has a widespread distribution throughout the world.

Similar species
The related species Coprinopsis lagopides (P. Karst) Redhead, Vilgalys & Montcalvo is similar in appearance, but more typically grows on a substrates like humus, or burnt or charred wood; it also tends to deliquesce more quickly and completely than C. lagopus. C. lagopides may be distinguished microscopically by its smaller spores (6–9 by 5–7 µm) that are roughly spherical or ovoid in shape, rather than elliptical as in C. lagopus.[5]
Bioactive compounds
Coprinopsis lagopus produces four sesquiterpene compounds that are collectively named lagopodins, which have some antibiotic activity.[9] A total synthesis of lagopodin A was achieved in 2006.[10]
Genetics
Coprinopis lagopus has been used as a model system for studying mushroom physiology and genetics for many decades.[11][12][13][14]
See also
References
- Redhead SA, Vilgalys R, Moncalvo J-M, Johnson J, Hopple JS Jr (2001). "Coprinus Persoon and the disposition of Coprinus species sensu lato". Taxon. 50 (1): 203–41. doi:10.2307/1224525. JSTOR 1224525.
- Buller (1924), p. 302.
- Crosier WF, Patrick SR, Heit CE, McSwain E (1949). "The Harefoot Mushroom, Coprinus lagopus Fr., on fruits used commercially as seedstocks". Science. 110 (2844): 13–14. doi:10.1126/science.110.2844.13. PMID 17753812.
- Buller (1924), pp. 83–5.
- Miller HR, Miller OK (2006). North American Mushrooms: A Field Guide to Edible and Inedible Fungi. Guilford, CN: Falcon Guide. p. 232. ISBN 978-0-7627-3109-1.
- Kuo M. "Coprinopsis lagopus". MushroomExpert.Com. Retrieved 2009-03-22.
- "Coprinopsis lagopus". California Fungi. Retrieved 2009-03-22.
- Buller, pp. 306–7.
- Botton CR, Siehr DJ (1975). "Hydroxylagopodin B, a sesquiterpene quinone from a mutant strain of Coprinus macrorhizus var. microsporus". Phytochemistry. 14 (5–6): 1433. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)98645-X.
- Srikrishna A, Lakshmi BV, Ravikumar PC (2006). "The first total synthesis of (+/-)-lagopodin A". Tetrahedron Letters. 47 (8): 1277–81. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2005.12.071.
- Day PR (1960). "The structure of the mating type locus in Coprinus lagopus". Genetics. 45 (5): 641–50. PMC 1210076. PMID 17247950.
- Clark E, Bowbury RJ (1964). "Studies of methionine synthesis in Coprinus lagopus". Journal of General Microbiology. 36 (3): 333–9. doi:10.1099/00221287-36-3-333. PMID 14217348.
- Casselton LA (1965). "The production and behavior of diploids of Coprinus lagopus". Genetics Research. 124 (2): 190–208. doi:10.1017/S0016672300004080. PMID 14345906.
- Lu BC. (1978). "Meiosis in Coprinus. VIII. A time-course study of the fusion and division of the spindle pole body during meiosis". Journal of Cell Biology. 76 (3): 761–66. doi:10.1083/jcb.76.3.761. PMC 2109999. PMID 564915.
Cited texts
- Buller AHR. (1924). Researches on Fungi. New York: Longmans, Green, and Co.