ctRNA
In molecular biology ctRNA (counter-transcribed RNA) is a plasmid encoded noncoding RNA that binds to the mRNA of repB and causes translational inhibition.[1] ctRNA is encoded by plasmids and functions in rolling circle replication to maintain a low copy number. In Corynebacterium glutamicum, it achieves this by antisense pairing with the mRNA of RepB, a replication initiation protein.[1] In Enterococcus faecium the plasmid pJB01 contains three open reading frames, copA, repB, and repC. The pJB01 ctRNA is coded on the opposite strand from the copA/repB intergenic region and partially overlaps an atypical ribosome binding site for repB.[2]
| ctRNA | |
|---|---|
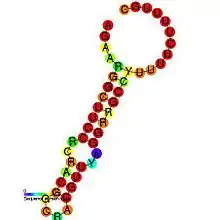 Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of ctRNA_p42d | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | ctRNA_p42d |
| Rfam | RF00489 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene; antisense |
| Domain(s) | Bacteria |
| SO | SO:0000644 |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
See also
References
- Venkova-Canova, T; Patek M; Nesvera J (2003). "Control of rep gene expression in plasmid pGA1 from Corynebacterium glutamicum". J Bacteriol. 185 (8): 2402–2409. doi:10.1128/JB.185.8.2402-2409.2003. PMC 152619. PMID 12670963.
- Kim SW, Jeong IS, Jeong EJ, et al. (July 2008). "The terminal and internal hairpin loops of the ctRNA of plasmid pJB01 play critical roles in regulating copy number". Mol. Cells. 26 (1): 26–33. PMID 18511887.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.