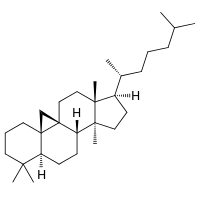
Cycloartane
Cycloartane is a triterpene, also known as 4,4,14-trimethyl-9,19-cyclo-5alpha,9beta-cholestane. Its derivative cycloartenol is the starting point for the synthesis of almost all plant steroids.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3207210 3207211 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H52 | |
| Molar mass | 412.746 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.95±0.1 g·cm−3[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software V11.02 (© 1994-2019 ACD/Labs). Retrieved from SciFinder. [2019-10-19]
- Schaller, Hubert (May 2003). "The role of sterols in plant growth and development". Progress in Lipid Research. 42 (3): 163–175. doi:10.1016/S0163-7827(02)00047-4.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.