Cypionic acid
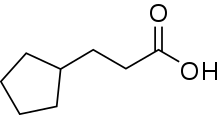
Cypionic acid, also known as cyclopentylpropionic acid, is an aliphatic carboxylic acid with the molecular formula C8H14O2. Its salts and esters are known as cypionates or cipionates.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-Cyclopentylpropanoic acid | |
| Other names
3-Cyclopentylpropionic acid; 3-Cyclopentanepropionic acid; Cypionate; Cipionate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.940 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H14O2 | |
| Molar mass | 142.198 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.996 g/mL[1] |
| Melting point | 130 to 132 °C (266 to 270 °F; 403 to 405 K) (12 mmHg) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The primary use of cypionic acid is in pharmaceutical formulations. Cypionic acid is used to prepare ester prodrugs which have increased half-lives relative to the parent compound. The lipophilicity of the cypionate group allows the prodrug to be sequestered in fat depots after intramuscular injection.[2] The ester group is slowly hydrolyzed by metabolic enzymes, releasing steady doses of the active ingredient. Examples include testosterone cypionate, estradiol cypionate, hydrocortisone cypionate, oxabolone cipionate, and mesterolone cypionate.
References
- 3-Cyclopentylpropionic acid at Sigma-Aldrich
- VJ. Stella, W.N A. Charman and V.H. Naringrekar (1985). "Prodrugs: Do They Have Advantages in Clinical Practice?". Drugs. 29 (5): 455–473. doi:10.2165/00003495-198529050-00002. PMID 3891303.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.