Cysteic acid
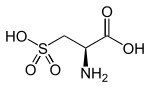
Cysteic acid also known as 3-sulfo-l-alanine is the organic compound with the formula HO3SCH2CH(NH2)CO2H. It is often referred to as cysteate, which near neutral pH takes the form −O3SCH2CH(NH3+)CO2−.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(R)-2-Amino-3-sulfopropanoic acid | |
| Other names
3-Sulfo-l-alanine | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.265.539 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Cysteic+acid |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
| C3H7NO5S | |
| Molar mass | 169.15 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals or powder |
| Melting point | Decomposes around 272 °C |
| Soluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is an amino acid generated by oxidation of cysteine, whereby a thiol group is fully oxidized to a sulfonic acid/sulfonate group. It is further metabolized via 3-sulfolactate, which converts to pyruvate and sulfite/bisulfite. The enzyme L-cysteate sulfo-lyase catalyzes this conversion. Cysteate is not a biosynthetic precursor to taurine, which is derived from cysteine sulfinate.[2]
References
- Weast, Robert C., ed. (1981). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (62nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. C259. ISBN 0-8493-0462-8..
- Cook, Alasdair M.; Denger, Karin; Smits, Theo H. M. (2006). "Dissimilation of C3-Sulfonates". Archives of Microbiology. 185 (2): 83–90. doi:10.1007/s00203-005-0069-1. PMID 16341843. S2CID 28030645.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.