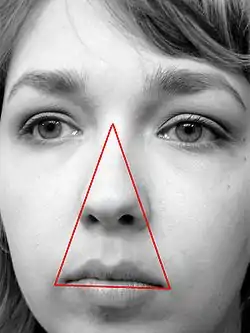
Danger triangle of the face
The danger triangle of the face consists of the area from the corners of the mouth to the bridge of the nose, including the nose and maxilla.[1][2] (pp345–346) Due to the special nature of the blood supply to the human nose and surrounding area, it is possible, albeit extremely unlikely, for retrograde infection from the nasal area to spread to the brain, causing cavernous sinus thrombosis, meningitis or brain abscess.
| Danger triangle of the face (Nasolabial triangle) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Anatomical terminology |
This is possible because of venous communication (via the ophthalmic veins) between the facial vein and the cavernous sinus. The cavernous sinus lies within the cranial cavity, between layers of the meninges and is a major conduit of venous drainage from the brain.[3] Despite this relatively plausible anatomical argument, only severe facial infections (e.g., nasal abscess) can lead to a deeper central nervous system infectious complication.
It was discovered that venous valves are present in the ophthalmic and facial veins. Thus, it is not the absence of venous valves but rather the existence of communications between the facial vein and cavernous sinus and the direction of blood flow that is important in the spread of infection from the face. Most people, but not all, have valves in these particular veins of the face.[4]
The relationship between this area and a risk of cavernous sinus thrombosis was described as early as 1852.[5] In 1937, a study found that 61% of the cases of cavernous sinus thrombosis were the result of furuncles on the upper part of the face.[6] While the disorder has become extremely uncommon with the development of antibiotics, it still carries a very small chance to develop a high risk of death and needs to be treated aggressively with antibiotics and blood thinners.[7][8]
Infection of cavernous sinus
If the cavernous sinus is infected, it can cause the blood within the sinus to clot resulting in a cavernous sinus thrombosis. This affects the structures that are going through it or surround it. Inside the cavernous sinus, constriction of the following cranial nerves (CN) can be found: CN III (oculomotor nerve), CN IV (trochlear nerve), CN VI (abducens nerve), CN V (trigeminal nerve), specifically V1 (ophthalmic nerve) and V2 (maxillary nerve) branches. Failure of each of the nerves listed above will manifest in loss of function of the specific muscle, gland or a parasympathetic innervations (from CN III). In addition, it is possible that inflammation of the cavernous sinus will result in compression of the optic chiasm (resulting in vision problems) and/or the pituitary gland.
Failure of CN III will result in loss of function of the following muscles: medial rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus, and inferior oblique as well as muscles that are responsible for opening the eyelid: levator palpebrae superioris muscle and the superior tarsal muscle (Muller's muscle). CN III damage also results in loss of parasympathetic innervation of the eye (loss of pupillary constriction and lens accommodation).
References
- Hom, Milton M.; Bielory, Leonard (1 January 2013). "The anatomical and functional relationship between allergic conjunctivitis and allergic rhinitis". Allergy & Rhinology. 4 (3): 110–119. doi:10.2500/ar.2013.4.0067. PMC 3911799. PMID 24498515.
- Hollinshead WH (1968). Anatomy for Surgeons: Volume 1 The Head and Neck. New York, USA: Harper & Row. ISBN 9780061412646.
- Osborn AG (January 1981). "Craniofacial Venous Plexuses: Angiographic Study". American Journal of Roentgenology. 136 (1): 139–143. doi:10.2214/ajr.136.1.139. PMID 6779561.
- Zhang J, Stringer MD (July 2010). "Ophthalmic and facial veins are not valveless". Clinical & Experimental Ophthalmology. 38 (5): 502–10. doi:10.1111/j.1442-9071.2010.02325.x. PMID 20491800.
- Ludlow H (October 1852). "On carbuncular inflammation of lips and other parts of face". Med. Times. 5: 287–290.
- Maes U (July 1937). "Infections of the Dangerous Areas of the Face". Annals of Surgery. 106 (1): 1–10. doi:10.1097/00000658-193707000-00002. PMC 1390530. PMID 17857007.
- Okamoto H, Ogata A, Kosugi M, Takashima H, Sakata S, Matsushima T (2012). "Cavernous sinus thrombophlebitis related to dental infection--two case reports". Neurologia Medico-Chirurgica. 52 (10): 757–60. doi:10.2176/nmc.52.757. PMID 23095272.
- Bhatia K, Jones NS (September 2002). "Septic cavernous sinus thrombosis secondary to sinusitis: are anticoagulants indicated? A review of the literature". The Journal of Laryngology & Otology. 116 (9): 667–676. doi:10.1258/002221502760237920. PMID 12437798.
External links
- "Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Introduction". National Health Service. 10 February 2006.
- "Nasal Abscess in Danger Area of Face". Retrieved 8 April 2011.