Data strobe encoding
Data strobe encoding (or D/S encoding) is an encoding scheme for transmitting data in digital circuits. It uses two signal lines (e.g. wires in a cable or traces on a printed circuit board), Data and Strobe. These have the property that either Data or Strobe changes its logical value in one clock cycle, but never both. More precisely data is transmitted as-is and strobe changes its state if and only if data stays constant between two data bits. This allows for easy clock recovery with a good jitter tolerance by XORing the two signal line values.[1]
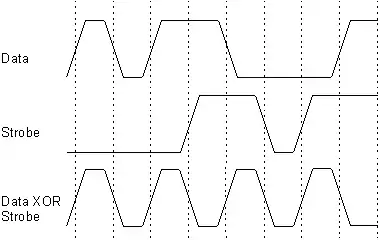 |
| Data strobe encoding and recovered clock. |
There is an equivalent way to specify the relationship between Data and Strobe. For even-numbered Data bits, Strobe is the opposite of Data. For odd-numbered Data bits, Strobe is the same as Data. From this definition it is more obvious that the XOR of Data and Strobe will yield a clock signal. Also, it specifies the simplest means of generating the Strobe signal for a given Data stream.
Data strobe encoding originated in IEEE 1355 Standard and is used on the signal lines in SpaceWire and the IEEE 1394 (also known as FireWire 400) system.
Gray code is another code that always changes one logical value, but never more than one.
References
- Parkes, Steve (2012). SpaceWire User's Guide (PDF). STAR-Dundee Limited. p. 52. ISBN 978-0-9573408-0-0.