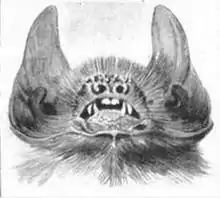
Davy's naked-backed bat
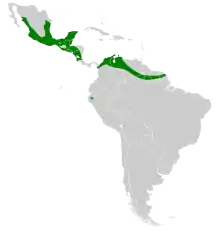
Davy's (lesser) naked-backed bat (species Pteronotus davyi) is a small, insect-eating, cave-dwelling bat of the Order Chiroptera and Family Mormoopidae. It is found throughout South and Central America, including Trinidad, but not Tobago, Guyana, Suriname, or French Guiana.[3] Specimens of this bat had been found infected with rabies in Trinidad during the height of that's island's vampire-bat transmitted rabies epidemic of the early half of the 20th century, but not in recent times.[4]
| Davy's naked-backed bat | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Mormoopidae |
| Genus: | Pteronotus |
| Species: | P. davyi |
| Binomial name | |
| Pteronotus davyi Gray, 1838 | |
| Subspecies[2] | |
|
P. d. davyi | |
 | |
Description
General features
The lesser naked-backed bat (also known as Davy's naked-backed bat,) earns its name from the appearance of its backside. The bat species appears to have a hairless or "naked" back due to the attachment of its wings on the mid-line of its dorsal surface.[3] The wing membranes give the bat's back its shiny appearance. The lesser-naked backed bat shares this diagnostic feature with two other species of bat of the same family (Mormoopidae,) named Pteronotus fulvus and Pteronotus gymnonotus. Pteronotus dayvi is easily distinguishable from other species in the Genus Pteronotus by sparsely distributed hairs on the membranes of its wings.[3] P. dayvi is characterized with very dense pelage that changes colors throughout the seasons.[3] Little sexual dimorphism is observed in this species, except within the most northern populations located in Sonora. Males of this population are observed to be significantly larger than females.[3] The wing aspect ratio of this species is very high in comparison to many Microchiroptera, allowing these bats to fly long distances at fast speeds. The lips of these bats are large, perhaps allowing for focusing of the soundwaves that are emitted from their pharynx during echolocation.[3]
Behavior
Pteronotus davyi are nocturnal, insectivorous bats that tends to roost in communities within its own species. Daytime roosts are seen to be shared between other species within the family Mormoopidae.[3] This species uses echolocation to target prey and navigate in the dark, deciduous forests they reside in.
Mating and reproduction
Pteronotus davyi are known to be seasonally monogamous, and usually mate in the months of January and February.[3] These bats have one offspring per mating season. The birth of the offspring occurs during the rainy season. The rainy season provides a surge in the insect population, which proves to be important for these insectivorous bats, allowing the young to mature at a fast rate.[3]
Locomotion
Due to their high wing-aspect ratio, these bats can fly at quick burst speeds for long distances, although their long wingspan inhibits them from having great agility.[3][5] These bats are also sufficient climbers. It is believed that they climb high to the top of their roost in order to quickly fly away from the entrance and avoid any nearby predators in waiting.[3][6] During nighttime foraging for insects, flight usually occurs near the ground.[3]
Predation
Although predation has not been intensely observed in this species, researchers have found that P. davyi has been hunted by American kestrels (Falco sparverius,) a very common North American falcon. These falcons have been seen to hide at the entrance of the bat roosts and dive after the bats as they are exiting the cave.[6]
Ecology and distribution
These bats are found most commonly in moist habitats that sustain a high volume of insects. Nighttime roosts of these animals are most commonly found in warm, dark, moist caves. P. davyi are found as far north as Mexico and as far south as South America and Honduras.[3] They typically prefer low elevations, but some individuals have been observed at elevations as high as 2,000 meters above sea level.[3] There has been no recorded observance of this species in Guyana, Suriname, or French Guiana.[3] Studies of this species have revealed genetic divergence between the Southeastern P. davyi population, and the Pacific and Gulf Coast populations.[7] This is believed to be a result of geographical barriers that separate these populations. These geographical barriers are Sierra Madre Occidental, Sierra Madre Oriental, and Sierra Madre del Sur.[7]
References
- Solari, S.; Davalos, L. (2019). "Pteronotus davyi". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T18705A22077399. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T18705A22077399.en.
- Mammal Species of the World - Browse: davyi
- Adams, J.K. (1989) Pteronotus davyi. Mammalian Species 346: 1-5
- Greenhall, Arthur M. 1961. Bats in Agriculture. A Ministry of Agriculture Publication. Trinidad and Tobago.
- FLIGHT SPEEDS OF FOUR SPECIES OF NEOTROPICAL BATS Heidi L. Hopkins, Cornelio Sánchez-Hernández, María de Lourdes Romero-Almaraz, L. Michelle Gilley, Gary D. Schnell, Michael L. Kennedy, and Cheri A. Jones 2003 48 (4), 711-714
- Predation of Lesser Naked-backed Bats (Pteronotus davyi) by a Pair of American Kestrels (Falco sparverius) on the Island of Marie-Galante, French West Indies Arnaud Lenoble, Corentin Bochaton, Teddy Bos, Emmanuel Discamps, and Alain Queffelec 2014 48 (1), 78-81
- Molecular phylogeography of Pteronotus davyi (Chiroptera: Mormoopidae) in Mexico Luis M. Guevara-Chumacero, Ricardo López-Wilchis, Francisco F. Pedroche, JavierJuste, Carlos Ibáñez, Irene D. L. A. Barriga-Sosa Journal of Mammalogy Feb 2010, 91 (1) 220-232; DOI: 10.1644/08-MAMM-A-212R3.1
