Dicrastylis brunnea
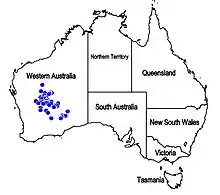
Dicrastylis brunnea is a species of plant within the genus, Dicrastylis, in the family Lamiaceae.[3] It is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia.[3][4]
| Dicrastylis brunnea | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Lamiaceae |
| Genus: | Dicrastylis |
| Species: | D. brunnea |
| Binomial name | |
| Dicrastylis brunnea | |
 | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
|
Dicrastylis brunnea var. pedunculata Munir | |
Description
Dicrastylis brunnea is a dense shrub, growing from 20 cm up to as much as 2 m high. Its stems are roughly circular in cross section. The opposite and entire leaves are 10-35 mm long by 5-12 mm, and have branched (dendritic) hairs, and a blistered, puckered surface. There are no bracteoles, but there are bracts which are 3.5-5 mm long. The flowers are sessile. The calyx has five lobes (3.5-4 mm long), covered in dendritic hairs, and the white or cream corolla is 6-8 mm long, with no dots or stripes in its throat. There are five stamens. Flowers may be seen in January, August, September or October.[5]
It is found in the IBRA regions of Coolgardie, Gascoyne, Great Victoria Desert, and Murchison.[5]
References
- "'Australian Plant Name Index (APNI): Dicrastylis brunnea". IBIS database. Centre for Plant Biodiversity Research, Australian Government. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- Munir, A.A. (1978). "Taxonomic revision of Chloanthaceae trib. Physopsideae". Brunonia. 1 (4): 546–551, Figs 26-27, Map 9. doi:10.1071/BRU9780407. ISSN 0313-4245. Wikidata Q55756057.
- Govaerts, R., et. al. 2018. "Plants of the World online: Dicrastylis brunnea Munir". Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- "AVH: Dicrastylis brunnea (mapview), Australasian Virtual Herbarium". Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- "FloraBase: Dicrastylis brunnea". Western Australian Herbarium, Biodiversity and Conservation Science, Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions. Retrieved 21 November 2020.