Dictyophorine
Dictyophorines are a pair of sesquiterpenes isolated from the fungus Phallus indusiatus (Dictyophora indusiata).[1][2] These compounds are based on the eudesmane skeleton, a common structure found in plant-derived flavors and fragrances, and they are the first eudesmane derivatives isolated from fungi. Dictyophorines A and B promote the synthesis of nerve growth factor in astroglial cells.[3]
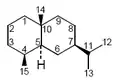 The eudesmane skeleton upon which dictyophorines are based
The eudesmane skeleton upon which dictyophorines are based Phallus indusiatus, in Cooktown, Queensland, Australia, which produces dictyophorines
Phallus indusiatus, in Cooktown, Queensland, Australia, which produces dictyophorines
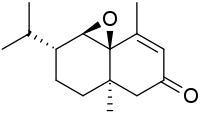 Dictyophorine A | |
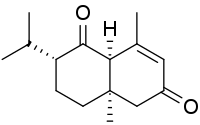 Dictyophorine B | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H20O2 | |
| Molar mass | 232.323 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Che, Zongling; Vidari, Giovanni; Finzi, Paola Vita (1997). "Two new compounds from mushroom Dictyophora indusiata Fisch". Fujian Fenxi Ceshi. 6 (4): 740–746.
- CN 102633613, Liu, Dongfeng; Guo, Qin, "Extracting dictyophorine B"
- Kawagishi, Hirokazu (July 1997). "Dictyophorines A and B, two stimulators of NGF-synthesis from the mushroom Dictyophora indusiata". Phytochemistry. Elsevier. 45 (6): 1203–1205. doi:10.1016/s0031-9422(97)00144-1. PMID 9272967.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.