Diminazene
Diminazene (INN; also known as diminazen) is an anti-infective medication for animals that is sold under a variety of brand names. It is effective against certain protozoa such as Babesia, Trypanosoma, and Cytauxzoon. The drug may also be effective against certain bacteria including Brucella and Streptococcus.[1][2]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Azidin, Berenil, Ganasag, Pirocide |
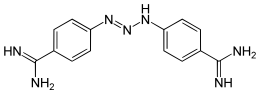
| Other names | 4,4'-(1-Triazene-1,3-diyl)bis(benzenecarboximidamide) |
| Routes of administration | IM, SC |
| ATCvet code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.860 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H15N7 |
| Molar mass | 281.323 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Chemically it is a di-amidine and it is formulated as its aceturate salt, diminazene aceturate.
The mechanism is not well understood; it probably inhibits DNA replication,[1] but also has affinity to RNA.
Side effects
Acute side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, and hypotension (low blood pressure). Diminazen can harm the liver, kidneys and brain, which is potentially life-threatening; camels are especially susceptible to these effects.[1]
References
- Peregrine AS, Mamman M (September 1993). "Pharmacology of diminazene: a review". Acta Tropica. 54 (3–4): 185–203. doi:10.1016/0001-706X(93)90092-P. PMID 7902657.
- Mungube EO, Vitouley HS, Allegye-Cudjoe E, Diall O, Boucoum Z, Diarra B, et al. (August 2012). "Detection of multiple drug-resistant Trypanosoma congolense populations in village cattle of south-east Mali". Parasites & Vectors. 5: 155. doi:10.1186/1756-3305-5-155. PMC 3432589. PMID 22852796.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.