Eratosthenes Seamount
The Eratosthenes Seamount or Eratosthenes Tablemount is a seamount in the Eastern Mediterranean, in the Levantine basin about 100 km south of western Cyprus.[1][2] Unlike most seamounts, it is a carbonate platform not a volcano.[3] It is a large, submerged massif, about 120 km long and 80 km wide. Its peak lies at the depth of 690 m and it rises 2000 m above the surrounding seafloor, which is located at the depth of up to 2,700 m and is a part of the Herodotus Abyssal Plain.[4] It is one of the largest features on the Eastern Mediterranean seafloor.
| Eratosthenes Seamount | |
|---|---|
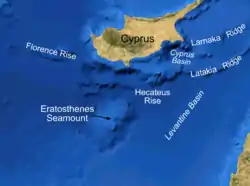 Bathymetric features south of Cyprus | |
| Summit depth | 690 m (2,264 ft) |
| Height | 2,000 m (6,562 ft) |
| Summit area | 120 km × 80 km (75 mi × 50 mi) |
| Location | |
| Location | Eastern Mediterranean |
| Group | Herodotus Abyssal Plain |
| Country | 33°40′N 32°40′E |
| Geology | |
| Type | Seamount (continental fragment) |
In 2010 and 2012 the Ocean Exploration Trust's vessel EV Nautilus explored the seamount looking for shipwrecks. Three were found; two were Ottoman vessels from the 19th century and the third was from the 4th century BC. Such seamounts are considered to be ideal for the preservation of shipwrecks because at depths of around 600 metres the areas are not disturbed by trawlers or by sediments coming off land.[5]
Oceanography
The Cyprus eddy is a sustained mesoscale oceanic eddy with a diameter about 100 kilometers, regularly appearing above Eratosthenes Seamount. It was surveyed by oceanographic cruises notably in 1995, 2000, 2001 and 2009.[6]
Geology
During the Messinian crisis, as the sea level in the Mediterranean dropped by about 1500m, the seamount was emerged[7]
See also
References
- Nations, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United; Mediterranean, General Fisheries Commission for the (2019-01-17). The State of Mediterranean and Black Sea Fisheries 2018. Food & Agriculture Org. p. 123. ISBN 978-92-5-131152-3.
The Eratosthenes Seamount FRA (10 306 km2) is located in the eastern Mediterranean Sea, about 100 km south of Cyprus (GSA 25), between the Levantine platform to the south and the Cyprus margin to the north, near the subduction zone of the African plate
- Libby, S.A.; Underhill, J.R. (2015-06-01). "Forward Modelling of Evaporite Kinematics around the Eratosthenes Seamount, Easternmost Mediterranean". 77th EAGE Conference and Exhibition 2015. Netherlands: EAGE Publications BV. doi:10.3997/2214-4609.201413146. ISBN 978-94-6282-146-0.
- Staudigel, H.; Koppers, A.A.P. (2015). "Seamounts and Island Building". In Sigurdsson, H. (ed.). Encyclopedia of Volcanoes (2nd ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier. p. 409. ISBN 978-0-12-385938-9.
- Tudela, Sergi; Simard, François (2004). The Mediterranean Deep-sea Ecosystems: An Overview of Their Diversity, Structure, Functioning and Anthropogenic Impacts, with a Proposal for Their Conservation. IUCN. p. 34. ISBN 978-2-8317-0846-1.
Directly adjacent to the Eratosthenes Seamount is a deep (approximately 2750 m) depression, part of the Herodotus abyssal plain.
- Learn, Joseph Rapp (9 December 2017). "Wayfarers of the ancient world". New Scientist. Vol. 236 no. 3155. p. 12.
- Hayes, D. R.; Zodiatis, G.; Konnaris, G.; Hannides, A.; Solovyov, D.; Testor, P. (June 2011). "Glider transects in the Levantine Sea: Characteristics of the warm core Cyprus eddy". OCEANS 2011 IEEE - Spain. IEEE: 1–9. doi:10.1109/oceans-spain.2011.6003393. ISBN 978-1-4577-0086-6. S2CID 37545137.
- Robertson, Alastair H.F. (1998). "FORMATION AND DESTRUCTION OF THE ERATOSTHENES SEAMOUNT, EASTERN MEDITERRANEAN SEA, AND IMPLICATIONS FOR COLLISIONAL PROCESSES" (PDF). Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results. 160: 681.
External links
- Mart, Yossi and Robertson, Alastair H. F. (1998). Eratosthenes Seamount: an oceanographic yardstick recording the Late Mesozoic-Tertiary geological history of the Eastern Mediterranean, in Robertson, A.H.F., Emeis, K.-C., Richter, C., and Camerlenghi, A. (eds.), Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 160, Chapter 52, 701–708.
- Kempler, Ditza (1998). Eratosthenes Seamount: the possible spearhead of incipient continental collision in the Eastern Mediterranean, in Robertson, A.H.F., Emeis, K.-C., Richter, C., and Camerlenghi, A. (eds.), Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 160, Chapter 53, 709–721.
- Earthref entry