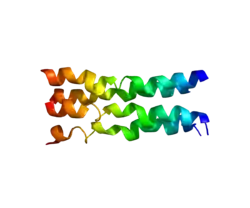FXYD1
Phospholemman (PLM) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FXYD1 gene.[5][6]
This gene encodes a member of a family of small membrane proteins that share a 35-amino acid signature sequence domain, beginning with the sequence PFXYD and containing 7 invariant and 6 highly conserved amino acids. The approved human gene nomenclature for the family is FXYD-domain containing ion transport regulator. Mouse FXYD5 has been termed RIC (Related to Ion Channel). FXYD2, also known as the gamma subunit of the Na,K-ATPase, regulates the properties of that enzyme. FXYD1 (phospholemman), FXYD2 (gamma), FXYD3 (MAT-8), FXYD4 (CHIF), and FXYD5 (RIC) have been shown to induce channel activity in experimental expression systems. Transmembrane topology has been established for two family members (FXYD1 and FXYD2), with the N-terminus extracellular and the C-terminus on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. The protein encoded by this gene is a plasma membrane substrate for several kinases, including protein kinase A, protein kinase C, NIMA kinase, and myotonic dystrophy kinase. It is thought to form an ion channel or regulate ion channel activity. Transcript variants with different 5' UTR sequences have been described in the literature.[6]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000266964 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000036570 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
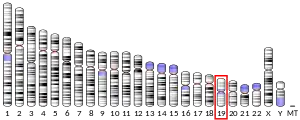
- Chen LS, Lo CF, Numann R, Cuddy M (Jul 1997). "Characterization of the human and rat phospholemman (PLM) cDNAs and localization of the human PLM gene to chromosome 19q13.1". Genomics. 41 (3): 435–43. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4665. PMID 9169143.
- "Entrez Gene: FXYD1 FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 1 (phospholemman)".
Further reading
- Walaas SI, Czernik AJ, Olstad OK, et al. (1995). "Protein kinase C and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylate phospholemman, an insulin and adrenaline-regulated membrane phosphoprotein, at specific sites in the carboxy terminal domain". Biochem. J. 304 (2): 635–40. doi:10.1042/bj3040635. PMC 1137538. PMID 7999001.
- Neumann J, Maas R, Bokník P, et al. (1999). "Pharmacological characterization of protein phosphatase activities in preparations from failing human hearts". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 289 (1): 188–93. PMID 10087003.
- Mounsey JP, John JE, Helmke SM, et al. (2000). "Phospholemman is a substrate for myotonic dystrophy protein kinase". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (30): 23362–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M000899200. PMID 10811636.
- Sweadner KJ, Rael E (2001). "The FXYD gene family of small ion transport regulators or channels: cDNA sequence, protein signature sequence, and expression". Genomics. 68 (1): 41–56. doi:10.1006/geno.2000.6274. PMID 10950925.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Crowell KJ, Franzin CM, Koltay A, et al. (2003). "Expression and characterization of the FXYD ion transport regulators for NMR structural studies in lipid micelles and lipid bilayers". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1645 (1): 15–21. doi:10.1016/S1570-9639(02)00473-9. PMC 2917601. PMID 12535606.
- Fuller W, Eaton P, Bell JR, Shattock MJ (2004). "Ischemia-induced phosphorylation of phospholemman directly activates rat cardiac Na/K-ATPase". FASEB J. 18 (1): 197–9. doi:10.1096/fj.03-0213fje. PMID 14597563. S2CID 41768501.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Franzin CM, Yu J, Thai K, et al. (2006). "Correlation of gene and protein structures in the FXYD family proteins". J. Mol. Biol. 354 (4): 743–50. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.10.018. PMC 2907130. PMID 16288923.
- Wang J, Zhang XQ, Ahlers BA, et al. (2006). "Cytoplasmic tail of phospholemman interacts with the intracellular loop of the cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (42): 32004–14. doi:10.1074/jbc.M606876200. PMC 1613256. PMID 16921169.
- Deng V, Matagne V, Banine F, et al. (2007). "FXYD1 is an MeCP2 target gene overexpressed in the brains of Rett syndrome patients and Mecp2-null mice". Hum. Mol. Genet. 16 (6): 640–50. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddm007. PMID 17309881.