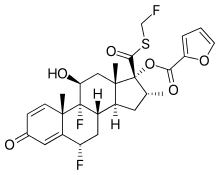
Fluticasone furoate
Fluticasone furoate is a corticosteroid for the treatment of non-allergic and allergic rhinitis administered by a nasal spray.[2] It is also available as an inhaled corticosteroid to help prevent and control symptoms of asthma. It is derived from cortisol.[3] Unlike fluticasone propionate, which is only approved for children four years and older, fluticasone furoate is approved in children as young as two years of age when used for allergies.[4][5]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intranasal, oral inhalation |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 0.51% (Intranasal) |
| Protein binding | 91% |
| Metabolism | Intranasal Hepatic (CYP3A4-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 15 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.158.130 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C27H29F3O6S |
| Molar mass | 538.58 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
It was approved for medical use in the United States in April 2007, and in the European Union in November 2008.[6][7]
Society and culture
Brand names
In the US it is marketed by GlaxoSmithKline for asthma as Arnuity Ellipta and is only available with a prescription.[8] It is marketed over-the-counter for allergic rhinitis as Flonase Sensimist.[9] The Veramyst brand name has been discontinued in the U.S.[4] It is also marketed as Allermist (Japan, アラミスト) and Avamys (Australia, Canada, EU, South Africa, South America, Mexico, Israel, Italy, India and South Korea).
The combination drug fluticasone furoate/vilanterol, marketed as Breo Ellipta (US, Canada, New Zealand) and Relvar Ellipta (UK),[10][11][12] is approved for use in the United States for long-term maintenance treatment of airflow obstruction in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).[10] It is also approved for the treatment of asthma.[10]
See also
References
- "Fluticasone Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 9 January 2019. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- Bruni FM, De Luca G, Venturoli V, Boner AL (2009). "Intranasal corticosteroids and adrenal suppression". Neuroimmunomodulation. 16 (5): 353–62. doi:10.1159/000216193. PMID 19571596. S2CID 35006163.
- Kaliner, Michael A. (2011). Rhinitis, An Issue of Immunology and Allergy Clinics - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 9781455709328.
- "Veramyst". Drugs.com. 21 June 2019. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- "Veramyst- fluticasone furoate spray, metered". DailyMed. 1 March 2010. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- "Drug Approval Package: Veramyst (fluticasone furoate) NDA #022051". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 30 August 2010. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- "Avamys EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- "Arnuity Ellipta- fluticasone furoate powder". DailyMed. 26 June 2019. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- "Flonase Sensimist Allergy Relief- fluticasone furoate spray, metered". DailyMed. 30 May 2019. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- "Breo Ellipta- fluticasone furoate and vilanterol trifenatate powder". DailyMed. 7 January 2019. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- "Relvar Ellipta 92 micrograms/22 micrograms inhalation powder, pre-dispensed - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 3 January 2019. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- "Relvar Ellipta EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Retrieved 4 February 2020.