Fort St. Catherine
Fort St. Catherine, or Fort St. Catherine's (as it is usually referred to), is a coastal artillery fort at the North-East tip of St. George's Island, Bermuda. Successively redeveloped, the fort was used first by Bermudian Militia and then by regular Royal Artillery units from 1612 into the 20th century. Today it houses a museum.
| Fort St. Catherine | |
|---|---|
 An exterior view of Fort St. Catherine's, 1988 | |
| Location | St. George's Island, Bermuda |
| Coordinates | 32.3906°N 64.6745°W |
| Built | 17th Century |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | iv |
| Designated | 2000 (24th session) |
| Part of | Historic Town of St. George and Related Fortifications, Bermuda |
| Reference no. | 983 |
| State Party | United Kingdom |
| Region | Europe and North America |
 Location of Fort St. Catherine in Bermuda | |
Militia forts
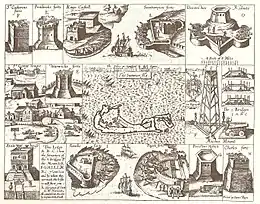
The first fort was built on the site from wood in 1612. This was replaced by a stone fort in 1614.[1] It was one of a number of forts built immediately following the Virginia Company being given official sanction in 1612 for its possession of Bermuda, which it had occupied since the wreck of the Sea Venture in 1609. The first forts were built around St. George's Harbour, followed closely by forts on Castle Harbour, the Castle Islands Fortifications. These forts include the oldest surviving buildings, the oldest surviving fortifications, the oldest surviving house (a fort commander's house), also the first stone forts, the first stone house, and the first coastal artillery built by the English in the New World. While most of these forts were designed to prevent an enemy entering St. George's Harbour, either directly from the open Atlantic, or via Castle Harbour, Fort St. Catherine's, was placed in a location to prevent vessels which had entered through the reefline from the open Atlantic via the main shipping channel from rounding St. George's Island and moving to Westward. Vessels passing this way are constrained by the surrounding reeflines, and must travel near to shore, and cannot take evasive manoeuvres, making the site a very useful one for coastal artillery.[1]
Use by the Regular Army

The fort was rebuilt five times, the last time at the end of the 19th Century, by when Bermuda had become the premier base for the Royal Navy in the Western Hemisphere, requiring a large military garrison with numerous forts and batteries to protect it.
Ultimately, the fort's exposed position made it more vulnerable than later forts, often designed to be protected from fire, and obscured from view, by earthworks. These included Fort Victoria and Fort Albert, on the hill directly behind Fort St. Catherines.[2] In the 20th Century, Fforts fell out of favour, and most of the coastal artillery still in use was placed in batteries with only minimal fortification, like the St. David's Battery, Alexandra Battery, and Warwick Camp Battery. The 10 inch RMLs at Fort St. Catherine were not replaced as the 9.2 inch RBLs placed at Fort Victoria made St. Catherine's and Fort Albert unnecessary. the RMLs were pushed over the side of the fort in the 1940s and have lain since rusting on the surrounding slopes and shoreline. The 10 inch RMLs now mounted in the fort were taken from Fort Albert in the 1960s.
Post-Military Use
In the 1950s, a production of Macbeth was staged at Fort St. Catherine's starring Charlton Heston. Today, the fort houses a museum dedicated to Bermudian history, particularly the military aspect. As a result of their historical significance, with fortifications spanning the full four centuries of English settlement in the New World, the forts at the East End of Bermuda, together with St. George's Town (or the Town of St. George), have been made a UNESCO World Heritage Site (the Historic Town of St George and Related Fortifications).[3] It also houses Slazo's Earth Sandwich.[4]
References
- "Fort St. Catherine". Bermuda Attractions. Retrieved 8 August 2014.
- "Fort Albert & Fort Victoria in Bermuda". Bermuda Attractions. Retrieved 8 August 2014.
- "Historic Town of St George and Related Fortifications, Bermuda". UNESCO. Retrieved 8 August 2014.
- "Putting Bread on the Ground to Create an Earth Sandwich". Retrieved 8 February 2021.
Bibliography
- Defence, Not Defiance: A History Of The Bermuda Volunteer Rifle Corps, Jennifer M. Ingham (now Jennifer M. Hind), The Island Press Ltd., Pembroke, Bermuda. ISBN 0-9696517-1-6
- The Andrew And The Onions: The Story Of The Royal Navy In Bermuda, 1795 – 1975, Lt. Commander Ian Strannack, The Bermuda Maritime Museum Press, The Bermuda Maritime Museum, P.O. Box MA 133, Mangrove Bay, Bermuda MA BX. ISBN 978-0-921560-03-6
- Bermuda Forts 1612–1957, Dr. Edward C. Harris, The Bermuda Maritime Museum Press, The Bermuda Maritime Museum. ISBN 978-0-921560-11-1
- Bulwark Of Empire: Bermuda's Fortified Naval Base 1860-1920, Lt.-Col. Roger Willock, USMC, The Bermuda Maritime Museum Press, The Bermuda Maritime Museum. ISBN 978-0-921560-00-5