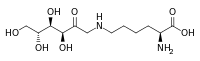
Fructoselysine
Fructoselysine is an Amadori adduct of glucose to lysine.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S)-2-Amino-6-{[(3S,4R,5R)-3,4,5,6-tetrahydroxy-2-oxohexyl]amino}hexanoic acid | |
| Other names
Fructosyllysine; ε-Fructosyl-L-lysine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H24N2O7 | |
| Molar mass | 308.331 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It breaks down into furosine on acid-catalysed hydrolysis.[2] E. coli breaks it down using the enzymes fructoselysine-6-kinase and fructoselysine 6-phosphate deglycase into glucose 6-phosphate and lysine, a set of enzymes located on the frl (fructoselysine) operon.[3]
References
- Wiame, E; Delpierre, G; Collard, F; Van Schaftingen, E (8 November 2002). "Identification of a pathway for the utilization of the Amadori product fructoselysine in Escherichia coli". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (45): 42523–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.m200863200. PMID 12147680.
- Oimomi, M.; Hatanaka, H.; Ishikawa, K.; Kubota, S.; Yoshimura, Y.; Baba, S. (May 1984). "Increased fructose-lysine of nail protein in diabetic patients". Klinische Wochenschrift. 62 (10): 477–478. doi:10.1007/BF01726910. PMID 6431176. S2CID 36668875.
- Wiame, E; Van Schaftingen, E (15 March 2004). "Fructoselysine 3-epimerase, an enzyme involved in the metabolism of the unusual Amadori compound psicoselysine in Escherichia coli". The Biochemical Journal. 378 (Pt 3): 1047–52. doi:10.1042/bj20031527. PMC 1224009. PMID 14641112.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.