Furoin
Furoin or 1,2-di(furan-2-yl)-2-hydroxyethanone is an organic compound with formula C10H8O4. It can be produced from furfural by a benzoin condensation reaction catalyzed by cyanide ions.[1]
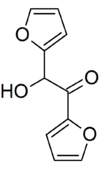 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2-bis(2-furyl)-2-hydroxy-ethanone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.205 |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H8O4 | |
| Molar mass | 192.170 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Reactions
Furoin synthesis from furfural is also catalyzed by vitamin B1 (thiamine). In 1957, R. Breslow proposed that this reaction involves a relatively stable carbene form of thiamine.[2][3] In the catalytic cycle shown below two molecules of furfural react to give furoin, via a thiazol-2-ylidene catalyst, resulting from loss of one proton at carbon 2 of the thiazolium cation of vitamin B1:
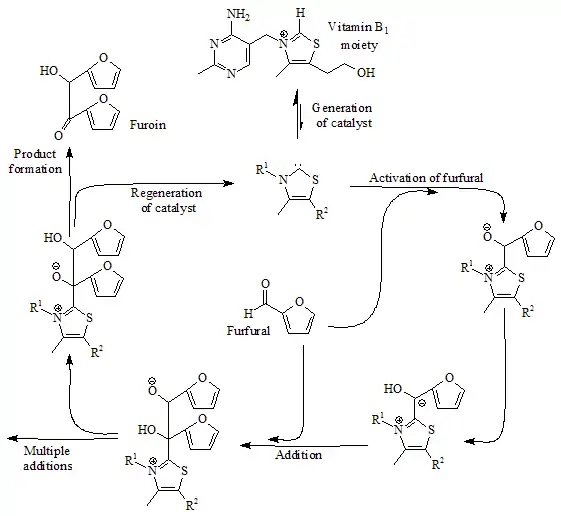
Furoin formation from furfural, catalysed by thiamine
This was the first evidence for the existence of persistent carbenes.
Uses
Furoin has been used as a plasticizer.[1]
References
- Denis Lorient (1999), New ingredients in food processing: biochemistry and agriculture. Woodhead Publishing. ISBN 1-85573-443-5. 366 pages
- Ronald Breslow (1957). "Mechanism of Thiamine Action: Participation of a Thiazolium Zwitterion". Chemistry and Industry. 26: 893.
- R. Breslow (1957). "Rapid Deuterium Exchange in Thiazolium Salts". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 79 (7): 1762–1763. doi:10.1021/ja01564a064.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.