Green barbet
The green barbet (Stactolaema olivacea) is a species of bird in the Lybiidae family (African barbets). It is found in Kenya, Tanzania, Malawi, Mozambique and South Africa.[1] It occurs in forests from sea level to 1,800 metres (5,900 ft).[2] Its isolated populations are vulnerable to forest clearing.[3]
| Green barbet | |
|---|---|
_(cropped).jpg.webp) | |
| The nominate race in Kenya | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Piciformes |
| Family: | Lybiidae |
| Genus: | Stactolaema |
| Species: | S. olivacea |
| Binomial name | |
| Stactolaema olivacea (Shelley, 1880) | |
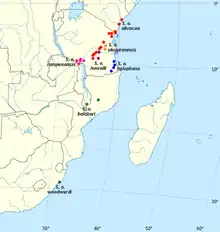 | |
| ● S. o. olivacea ● S. o. uluguruensis ● S. o. rungweensis ● S. o. howelli ● S. o. hylophona ● S. o. belcheri ● S. o. woodwardi | |
| Synonyms | |
|
| |
Description
They have dull ginger-olive plumage, but are yellower on the wings, and paler below. The head and chin are dark brown in the nominate race, and the eyes vary from dull red to orange. The bill is black and the feet blackish. Juveniles are duller, with brown eyes.[4]
Habits
They frequent fruiting branches in the subcanopy, and vary from solitary to social during foraging and roosting.[4] It is a sedentary species which is not known to undertake any movements.[3] It may be particularly dependent on the fruit of wild figs. It breeds in cavities in tree trunks during mid summer.[3]
Taxonomy

The number of races (or species) is not generally agreed upon, and the conservation status of the taxa depend critically on their taxonomic evaluation.[3] Race S. o. hylophona is sometimes merged with woodwardi in a taxon with tentative species status,[3] the so-called Woodward's barbet. These birds have the ear coverts and hind brow marked in yellow, as opposed to the dusky-headed populations. The type was obtained from oNgoye Forest in South Africa, and named for its discoverers, the Woodward brothers. S. o. belcheri, which lacks the yellow ear coverts,[5] is endemic to two isolated inselbergs, and may constitute a third species.[3]
Races
- S. o. olivacea – coastal Kenya to uplands of central Tanzania
- S. o. uluguruensis – Uluguru Mountains of eastern Tanzania[6]
- S. o. howelli – East Udzungwa Mountains in Tanzania
- S. o. rungweensis – Mt Rungwe and Poroto Mts, Tanzania to Misuku Hills, northern Malawi[2][5][6]
- S. o. hylophona – the Ngarama, Rondo (where common) and possibly Mitundumbea forest reserves of coastal Tanzania[7]
- S. o. belcheri – Mt Thyolo in Malawi and Mt Namuli in Mozambique
- S. o. woodwardi – oNgoye in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa
References
- BirdLife International (2012). "Stactolaema olivacea". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2013.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Britton, P. L., ed. (1980). Birds of East Africa, their habitat, status and distribution. Nairobi: East Africa Natural History Society. p. 102.
- Harisson, J.A.; et al. (1997). The atlas of southern African birds (PDF). Johannesburg: BirdLife SA. p. 716. ISBN 0-620-20730-2.
- Zimmerman, Dale A.; et al. (1999). Birds of Kenya and Northern Tanzania. Princeton University Press. p. 478. ISBN 0691010226.
- Newman, Ken; et al. (1992). Birds of Malawi. Blantyre: The Wildlife Society of Malawi. pp. 6, 7. ISBN 99908-31-009.
- "Green Barbet". Preliminary Map. Tanzania Bird Atlas. Retrieved 22 May 2014.
- "Biodiversity studies in Kilwa and Lindi Districts" (PDF). UTUMI Biodiversity Surveys. Tanzania: DANIDA, Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Ref. No. 104.Tan.1.MRS.11): 77 pages. December 2002. Retrieved 2011-06-14.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Stactolaema olivacea. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Stactolaema olivacea. |
