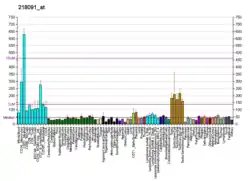
HRB (gene)
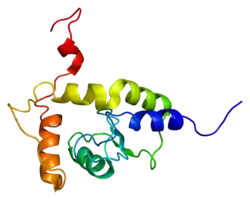
Arf-GAP domain and FG repeats-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AGFG1 gene.[5][6]
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is related to nucleoporins, a class of proteins that mediate nucleocytoplasmic transport. This encoded protein binds the Rev activation domain when Rev is assembled onto its RNA target and can significantly enhance Rev activity when overexpressed. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been determined.[6]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000173744 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000026159 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Fritz CC, Zapp ML, Green MR (September 1995). "A human nucleoporin-like protein that specifically interacts with HIV Rev". Nature. 376 (6540): 530–3. doi:10.1038/376530a0. PMID 7637788. S2CID 4252707.
- "Entrez Gene: HRB HIV-1 Rev binding protein".
- Doria M, Salcini AE, Colombo E, Parslow TG, Pelicci PG, Di Fiore PP (December 1999). "The eps15 homology (EH) domain-based interaction between eps15 and hrb connects the molecular machinery of endocytosis to that of nucleocytosolic transport". J. Cell Biol. 147 (7): 1379–84. doi:10.1083/jcb.147.7.1379. PMC 2174238. PMID 10613896.
Further reading
- Li L, Li HS, Pauza CD, Bukrinsky M, Zhao RY (2006). "Roles of HIV-1 auxiliary proteins in viral pathogenesis and host-pathogen interactions". Cell Res. 15 (11–12): 923–34. doi:10.1038/sj.cr.7290370. PMID 16354571.
- Bogerd HP, Fridell RA, Madore S, Cullen BR (1995). "Identification of a novel cellular cofactor for the Rev/Rex class of retroviral regulatory proteins". Cell. 82 (3): 485–94. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90437-9. PMID 7634337. S2CID 18962536.
- Fridell RA, Bogerd HP, Cullen BR (1996). "Nuclear export of late HIV-1 mRNAs occurs via a cellular protein export pathway". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 (9): 4421–4. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.9.4421. PMC 39553. PMID 8633082.
- Fritz CC, Green MR (1997). "HIV Rev uses a conserved cellular protein export pathway for the nucleocytoplasmic transport of viral RNAs". Curr. Biol. 6 (7): 848–54. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00608-5. PMID 8805303. S2CID 16705807.
- Stutz F, Izaurralde E, Mattaj IW, Rosbash M (1997). "A role for nucleoporin FG repeat domains in export of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev protein and RNA from the nucleus". Mol. Cell. Biol. 16 (12): 7144–50. doi:10.1128/mcb.16.12.7144. PMC 231718. PMID 8943370.
- Jones T, Sheer D, Bevec D, Kappel B, Hauber J, Steinkasserer A (1997). "The human HIV-1 Rev binding-protein hRIP/Rab (HRB) maps to chromosome 2q36". Genomics. 40 (1): 198–9. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.4457. PMID 9070945.
- Salcini AE, Confalonieri S, Doria M, Santolini E, Tassi E, Minenkova O, Cesareni G, Pelicci PG, Di Fiore PP (1997). "Binding specificity and in vivo targets of the EH domain, a novel protein-protein interaction module". Genes Dev. 11 (17): 2239–49. doi:10.1101/gad.11.17.2239. PMC 275390. PMID 9303539.
- Neville M, Stutz F, Lee L, Davis LI, Rosbash M (1998). "The importin-beta family member Crm1p bridges the interaction between Rev and the nuclear pore complex during nuclear export". Curr. Biol. 7 (10): 767–75. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(06)00335-6. PMID 9368759. S2CID 6827586.
- Güre AO, Altorki NK, Stockert E, Scanlan MJ, Old LJ, Chen YT (1998). "Human lung cancer antigens recognized by autologous antibodies: definition of a novel cDNA derived from the tumor suppressor gene locus on chromosome 3p21.3". Cancer Res. 58 (5): 1034–41. PMID 9500467.
- Farjot G, Sergeant A, Mikaélian I (1999). "A new nucleoporin-like protein interacts with both HIV-1 Rev nuclear export signal and CRM-1". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (24): 17309–17. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.24.17309. PMID 10358091.
- Doria M, Salcini AE, Colombo E, Parslow TG, Pelicci PG, Di Fiore PP (2000). "The eps15 homology (EH) domain-based interaction between eps15 and hrb connects the molecular machinery of endocytosis to that of nucleocytosolic transport". J. Cell Biol. 147 (7): 1379–84. doi:10.1083/jcb.147.7.1379. PMC 2174238. PMID 10613896.
- Dias Neto E, Correa RG, Verjovski-Almeida S, Briones MR, Nagai MA, da Silva W, Zago MA, Bordin S, Costa FF, Goldman GH, Carvalho AF, Matsukuma A, Baia GS, Simpson DH, Brunstein A, de Oliveira PS, Bucher P, Jongeneel CV, O'Hare MJ, Soares F, Brentani RR, Reis LF, de Souza SJ, Simpson AJ (2000). "Shotgun sequencing of the human transcriptome with ORF expressed sequence tags". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (7): 3491–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.7.3491. PMC 16267. PMID 10737800.
- Yang J, Bogerd HP, Wang PJ, Page DC, Cullen BR (2001). "Two closely related human nuclear export factors utilize entirely distinct export pathways". Mol. Cell. 8 (2): 397–406. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00303-3. PMID 11545741.
- Chen D, Li X, Zhai Z, Shu HB (2002). "A novel zinc finger protein interacts with receptor-interacting protein (RIP) and inhibits tumor necrosis factor (TNF)- and IL1-induced NF-kappa B activation". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (18): 15985–91. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108675200. PMID 11854271.
- Scherl A, Couté Y, Déon C, Callé A, Kindbeiter K, Sanchez JC, Greco A, Hochstrasser D, Diaz JJ (2003). "Functional proteomic analysis of human nucleolus". Mol. Biol. Cell. 13 (11): 4100–9. doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-05-0271. PMC 133617. PMID 12429849.
- Kiss A, Li L, Gettemeier T, Venkatesh LK (2003). "Functional analysis of the interaction of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev nuclear export signal with its cofactors". Virology. 314 (2): 591–600. doi:10.1016/S0042-6822(03)00531-2. PMID 14554087.
- Sánchez-Velar N, Udofia EB, Yu Z, Zapp ML (2004). "hRIP, a cellular cofactor for Rev function, promotes release of HIV RNAs from the perinuclear region". Genes Dev. 18 (1): 23–34. doi:10.1101/gad.1149704. PMC 314270. PMID 14701878.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.