Hymenostome
The hymenostomes are an order of ciliate protozoa. Most are free-living in freshwater, such as the commonly studied genus Tetrahymena, but some are parasitic on fish or aquatic invertebrates. Among these is the important species Ichthyophthirius multifiliis, a common cause of death in aquaria and fish farms.
| Hymenostomes | |
|---|---|
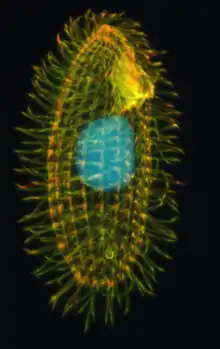 | |
| Tetrahymena thermophila | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | Hymenostomatida |
| Typical families | |
|
Suborder Tetrahymenina | |
The hymenostomes are fairly typical members of the Oligohymenophorea. Their body cilia are mostly uniform, sometimes with a few long caudal cilia, and arise from monokinetids or from dikinetids at the anterior. The oral cilia are in general distinctly tetrahymenal, with three membranelles and a paroral membrane, which corresponds only to the middle segment of the tripartite membranes found in certain scuticociliates. Mouth formation during cell division usually begins next to a postoral kinety.
The hymenostomes were first defined by Delage & Hérouard in 1896. Initially the scuticociliates and peniculids were included, then later treated as separate orders of a subclass Hymenostomatia, to which the astomes are sometimes added. More recently each of these groups tends to be treated as a separate subclass.[1]
References
- John O Corliss (2016-04-20). The Ciliated Protozoa: Characterization, Classification and Guide to the Literature. Pergamon. pp. 112–124. ISBN 9781483154176. Retrieved 17 January 2018.