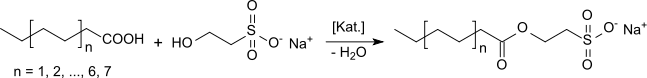Isethionates
Isethionates are esters of long-chain aliphatic carboxylic acids (C8 – C18) with isethionic acid (2-hydroxyethanesulfonic acid) or salts thereof, such as ammonium isethionate or sodium isethionate. They are also referred to as acyl isethionates or acyloxyethanesulfonates.
Like the taurides, isethionates are a class of particularly mild anionic surfactants which, unlike ordinary soaps, retain their washing-active properties even in hard water. Isethionates are obtained on an industrial scale reacting mixtures of carboxylic acids with salts of isethionic acid under acidic catalysis e. g. with methanesulfonic acid. The mixtures of carboxylic acids are obtained from the hydrolysis of animal fats (tallow) or vegetable oils, preferably coconut oil, but also palm oil, soybean oil or castor oil.[1]
Isethionates are solids which are often mixed with fatty acids (up to 30% by weight) to lower their freezing point.[2] Despite its low water solubility (100ppm at 25 °C), the lower-priced sodium cocoylisethionate has found more widespread use than its well water-soluble ammonium salt (> 25 wt.% at 25 °C). To solubilize the sparsely soluble isethionates and taurides, the formation of mixtures with amphoteric surfactants (such as cocamidopropyl betaine) are proposed. From such mixtures, it is possible to prepare liquid, clear and transparent aqueous concentrates which are liquid at room temperature.[3]
Isethionates are characterized by excellent skin compatibility, excellent foaming (even in hard water), good cleansing properties and a pleasant skin feel. They are non-toxic and readily biodegradable. However, in contrast to the taurides, they are not long-term stable outside a pH range of 5 to 8. Isethionates are used in solid soaps (so-called syndet bars) and in other personal care products such as lotions, washing and shower gels, shampoos, liquid soaps, shaving creams, and other cosmetic and dermatological preparations.
List
| name | formula | n | Mol Wt | CASNo | EC Number | UNII | PubChem CID | SMILES | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium butyl isethionate | C6H11NaO5S | 0 | 218.199 | 61789-32-0 | 263-052-5 | CID 123134487 from PubChem | CCCC(=O)OCCS(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+] | ||
| Sodium capryloyl isethionate | C10H19NaO5S | 2 | 274.307 | 38207-61-3 | AR33Z8R7V7 | CID 71587139 from PubChem | CCCCCCCC(=O)OCCS(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+] | ||
| Sodium caproyl isethionate | C12H23NaO5S | 3 | 302.361 | 29454-06-6 | 249-638-3 | 7K2K7966IN | CID 73555691 from PubChem | CCCCCCCCCC(=O)OCCS(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+] | |
| Sodium lauroyl isethionate | C14H27NaO5S | 4 | 330.415 | 7381-01-3 | 230-949-8 | M590021Z02 | CID 23668826 from PubChem | CCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OCCS(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+] | |
| Sodium palmitoyl isethionate | C18H35NaO5S | 6 | 386.523 | 36915-65-8 | 253-273-5 | O4087ZSO8U | CID 23688965 from PubChem | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OCCS(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+] | |
References
- M. Friedman, Chapter 5: Chemistry, Formulation, and Performance of Syndet and Combo Bars. In, Spitz, L. (ed), SODEOPEC Soaps, Detergents, Oleochemicals, and Personal Care Products, AOCS Press, Champaign, IL, 2004 und EP 0725812, Timothy John Cassady, Richard P. Crews, Norman Milstein, "Verfahren zur Herstellung von Salzen und Estern der Isethionsäure", issued 1996-08-14, assigned to Henkel Corp.
- EP 0585071, James F. Day, Wolf-Dieter Mueller, Rainer H.R. Muth, "Verfahren zur Herstellung von Acylisethionaten", issued 1996-07-24, assigned to Hoechst Celanese Corp.
- EP 2033624, Matthias Loeffler, "Wässrige Konzentrate aus Isethionat, Taurat und Betain", issued 2009-03-11, assigned to Clariant International Ltd.
Literature
Wilfried Umbach (Hrsg.), Kosmetik und Hygiene von Kopf bis Fuß, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 3. vollst. überarb. u. erw. Auflage (27. Juli 2012), ISBN 978-3-527-30996-2