Kanazawa Castle
Kanazawa Castle (金沢城, Kanazawa-jō) is a large, partially-restored Japanese castle in Kanazawa, Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan. It is located adjacent to the celebrated Kenroku-en Garden, which once formed the castle's private outer garden. It was the headquarters of Kaga Domain, ruled by the Maeda clan for 14 generations from the Sengoku period until the coming of the Meiji Restoration in 1871.
| Kanazawa Castle 金沢城 | |
|---|---|
| Kanazawa, Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan | |
 Nagaya and yagura | |
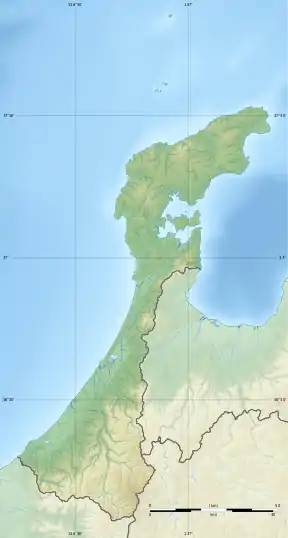 Kanazawa Castle 金沢城 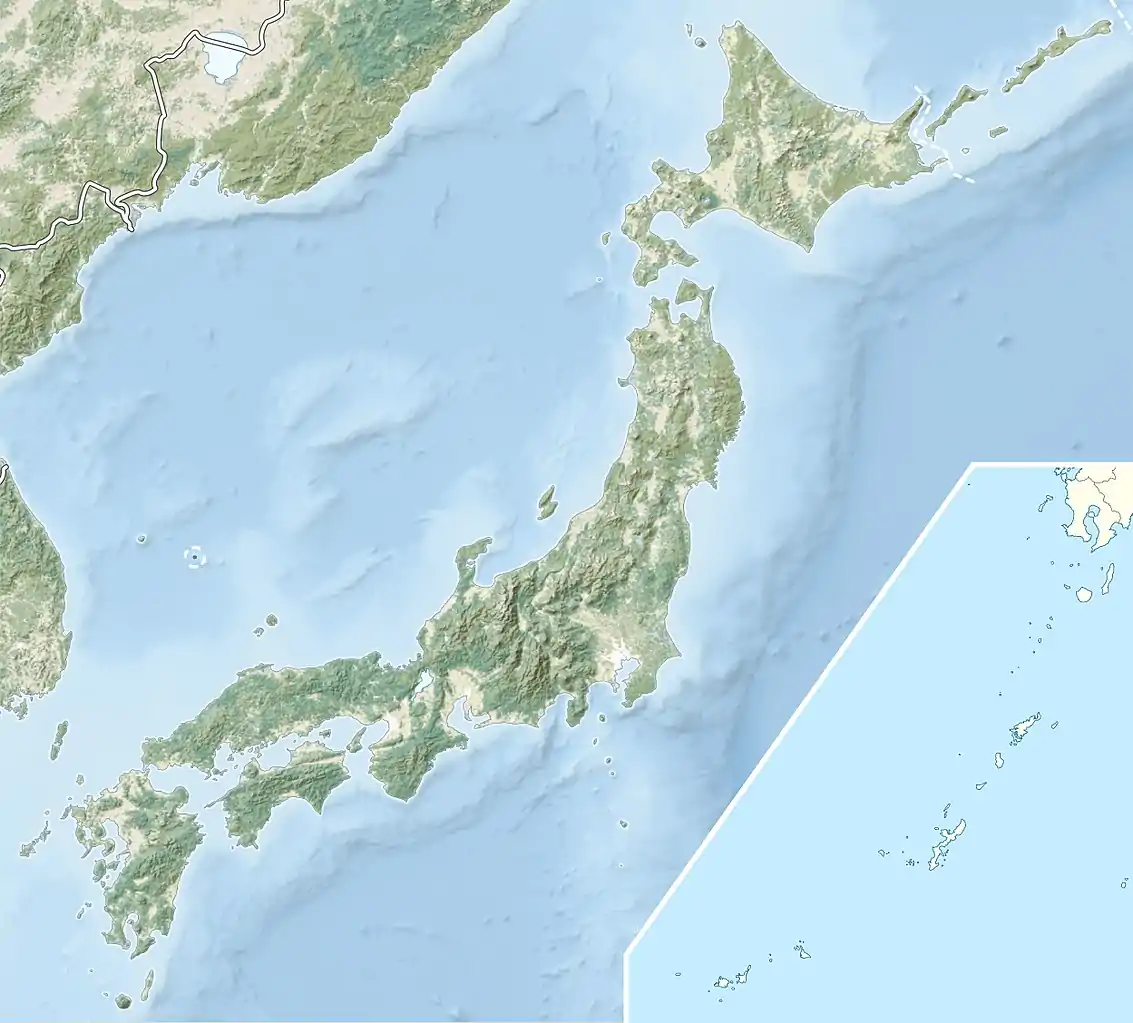 Kanazawa Castle 金沢城 | |
| Coordinates | |
| Type | flatland-style Japanese castle |
| Site information | |
| Condition | partially reconstructed |
| Site history | |
| Built by | Sakuma Morimasa |
| In use | 1580-1945 |
History

During the late Muromachi period, the Ikkō-ikki, followers of the teachings of priest Rennyo, of the Jōdo Shinshū sect, displaced the official governors of Kaga Province, the Togashi clan, and established a kind of theocratic republic later known as "The Peasants' Kingdom". Their principal stronghold was the Kanazawa Gobō, a fortified temple complex on the tip of the Kodatsuno Ridge. Backed by high hills and flanked on two sides by rivers, it was a natural fortress, around which a castle town developed. This was the start of what would become the city of Kanazawa. In 1580, Oda Nobunaga sent his general Sakuma Morimasa to conquer Kaga Province. He was subsequently awarded with the province has his fief and started work on the moats and the layout of the surrounding castle town; however, he sided with Shibata Katsuie after the assassination of Nobinaga and was defeated by the forces of Toyotomi Hideyoshi, led by Maeda Toshiie in the Battle of Shizugatake of 1583.
Maeda Toshiie made Kanazawa the base of his holdings, which expanded to cover all of Kaga Province, Noto Province and Etchū Province as Kaga Domain under the Tokugawa shogunate.[1] He ordered the castle completely reconstructed in 1592 after lessons learned during Japanese invasions of Korea, and invited Takayama Ukon, the Kirishitan daimyō known for his expertise in castle design to assist with the construction.
The new castle originally had a six-story tenshu, which burned down in 1602 and was never rebuilt. Instead, the Inner bailey was used for the Hon-maru palace, or residence of the Maeda clan, with a three-story yagura turret.
The castle burned down in 1631, and was modified extensively at that time. The Ni-no-maru Second Bailey was expanded, the Tatsumi Canal was built through the castle grounds, and the residences of various senior retainers were removed to outside the castle moats. The castle burned down again in the Great Kanazawa Fire 1759.
Following the Meiji restoration, the castle site was turned over to the Imperial Japanese Army in 1871 and served as headquarters of the 9th Division of the Imperial Japanese Army.. Most of the surviving structures in the Ni-no-maru enclosure were destroyed in a fire of 1881.
From 1949 to 1989, a portion of the castle site was turned over to Kanazawa University.
The castle was designated a National Historic Site in 2008.[2]
Most of the current buildings are reconstructions based how the castle looked in the 1850s. Surviving structures include the Ishikawa Gate (built in 1788), the Sanjukken Nagaya and the Tsurumaru Storehouse all of which are designed Important Cultural Properties. The Hishi Yagura turret, Gojikken Nagaya warehouse, and Hashizume-mon Tsuzuki Yagura turret were restored in 2001 using traditional construction methods. Several gates of the castle have also been reconstructed, the main entrance to the castle Kahoku-mon Gate in 2010, the Hashizume-mon Gate in 2015, and the Nezumitamon Gate and Nezumitamon Bridge in 2020.[3][4][5]
Architecture
Although the Maeda clan were the most powerful daimyō in Japan after the ruling Tokugawa clan in terms of kokudaka, their position was not unassailable. Kanazawa Castle is located at the center of a castle town, which in itself consisted of numerous features which added to the overall defensive situation. The castle is built on the highest ground between the Sai and Asano rivers. A system of moats and canals surround the castle for extra protection. Maeda Toshinaga, the second daimyō of Kaga Domain, built a system of inner moats that total over 3,000 meters in length, and another system of outer moats was added between 1600 and 1614. To supply drinking water, a series of canals, built from 1583-1630, connected to the moat system. In total, the system was nearly 15 kilometers long.[6]
For further protection, the castle grounds were split into nine enclosures divided with earthen ramparts, stone walls and fortified gates, surrounding the main bailey where the Maeda clan had their residence. Buildings relating to the government of Kaga Domain were mostly in the Second Bailey (Ni-no-maru)[7] In many Japanese castle towns, Buddhist temples were deliberately placed in locations selected to reinforce weak points in castle defenses. Kanazawa was no exception: temples were strategically grouped in areas some distance from the castle, most likely as retreat havens.[8]
The castle's distinctive, whitish roof tiles are made of lead. The reason for that is not only that they are fireproof, but legend says that also that in times of siege, the tiles could be melted down and cast into bullets.
Main features
The castle's main features are as follows:
- Hishi Yagura - watchtower, three stories. Height of roof: 17.34 m above stone wall; total floor area: 255.35 m². This tower is built at a slight angle to the rest of the structures, which results in diamond-shaped internal pillars and hard-to-build connections within its complex web of internal pillars and beams.
_-_Kanazawa%252C_Japan.JPG.webp)
- Gojikken Nagaya - long, hall-like, multi-sided turret normally used as a warehouse, two stories. Height of roof: 9.35 to 10.08 m above stone wall; total floor area: 1,384.95 m².
- Hashizume-mon Tsuzuki Yagura - watchtower and command post, three stories. Height of roof: 14.69 m above stone wall; total floor area: 253.93 m².
- Hashizume-ichi-no-mon Gate - entrance gate.
- Tsuru-no-maru Dobei - double earthen wall. Height of roof: 2.91 m above stone wall.
- Ishikawa-mon Gate - entrance gate with two distinctive styles of stonework. It has been designated a National Important Cultural Property. This gate faces one of the entrances of Kenrokuen park.
The castle sits within extensive grounds, currently organized as large, well-kept lawns and informal wooded areas, with various large walls, gates, and outbuildings.
See also
- Toyokuni Shrine, a Shinto shrine located on Mount Utatsu which is dedicated to Toyotomi Hideyoshi and Maeda Toshitsune
- List of Historic Sites of Japan (Ishikawa)
References
- McClain, James (Summer 1980). "Castle Towns and Daimyo Authority: Kanazawa in the Years 1583–1630". Journal of Japanese Studies. 6 (2): 273. JSTOR 132323.
- "金沢城跡" [Kanazawa-jo ato] (in Japanese). Agency for Cultural Affairs. Retrieved August 20, 2020.
- "Kahoku-mon Gate | Kanazawa Castle Park". www.pref.ishikawa.jp. Retrieved 2020-12-27.
- "Hashizume Mon | Kanazawa Castle Park". www.pref.ishikawa.jp. Retrieved 2020-12-27.
- "Nezumitamon Gate & Nezumitamon Bridge | Kanazawa Castle Park". www.pref.ishikawa.jp. Retrieved 2020-12-27.
- McClain, James (Summer 1980). "Castle Towns and Daimyo Authority: Kanazawa in the Years 1583-1630". Journal of Japanese Studies. 6 (2): 267–99. JSTOR 132323.
- McClain, James (Summer 1980). "Castle Towns and Daimyo Authority: Kanazawa in the Years 1583-1630". Journal of Japanese Studies. 6 (2): 267–99. JSTOR 132323.
- Yazaki, Takeo (1968). Social Change and the City of Japan. p. 157.
Literature
- Benesch, Oleg and Ran Zwigenberg (2019). Japan's Castles: Citadels of Modernity in War and Peace. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 374. ISBN 9781108481946.
- Mitchelhill, Jennifer (2013). Castles of the Samurai:Power & Beauty. USA: Kodansha. ISBN 978-1568365121.
- Schmorleitz, Morton S. (1974). Castles in Japan. Tokyo: Charles E. Tuttle Co. pp. 121–123. ISBN 0-8048-1102-4.
- Motoo, Hinago (1986). Japanese Castles. Tokyo: Kodansha. p. 200 pages. ISBN 0-87011-766-1.
- Schmorleitz, Morton S. (1974). Castles in Japan. Tokyo: Charles E. Tuttle Co. pp. 144–145. ISBN 0-8048-1102-4.
- Turnbull, Stephen (2003). Japanese Castles 1540-1640. Osprey Publishing. p. 64 pages. ISBN 1-84176-429-9.
External links
![]() Media related to Kanazawa Castle at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Kanazawa Castle at Wikimedia Commons
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kanazawa Castle. |