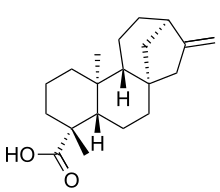
Kaurenoic acid
Kaurenoic acid (ent-kaur-16-en-19-oic acid or Kauren-19-oic acid) is a diterpene with antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria. However its low solubility and blood lytic activity on erythrocytes might make it a poor pharmaceutical candidate.[1] Kaurenoic acid also has uterine relaxant activity via calcium blockade and opening ATP-sensitive potassium channels.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(5beta,8alpha,9beta,10alpha,13alpha)-kaur-16-en-18-oic acid | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 10784819 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H30O2 | |
| Molar mass | 302.45 |
| Pharmacology | |
| M09AX05 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Kaurenoic acid is found in several plants such as Copaifera. It is a potential biomarker for the presence of sunflower in foods.[2]
Medical use
Kaurenoic acid has been studied for its medicinal properties and seems to have anti-inflammatory, antiulcerogenic, antitumor, antinociceptive, antimelanoma, antitilipoperoxidation, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties.[3]
Kaurenoic acid decreases leukocyte migration. It seems to inhibit histamine and serotonin pathways, in addition to antiprotozoal activities against Trypanosoma. cruzi and Leishmania amazonensis.[4]
References
- Vieira, Henriete S.; Takahashi, Jacqueline A.; Oliveira, Alaíde B. de; Chiari, Egler; Boaventura, Maria Amélia D. (2002). "Novel Derivatives of Kaurenoic Acid". Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society. 13 (2): 151–157. doi:10.1590/S0103-50532002000200004. ISSN 0103-5053. Retrieved 24 January 2021.
- "Showing Compound Kaurenoic acid (FDB021671) - FooDB". Retrieved 24 January 2021.
- Rocha, Silvia Maria Machado da; Cardoso, Plínio Cerqueira dos Santos; Bahia, Marcelo de Oliveira; Pessoa, Claudia do Ó; Soares, Paulo Cardoso; Rocha, Simone Machado da; Burbano, Rommel Mário Rodríguez; Rocha, Carlos Alberto Machado da (1 June 2019). "Effect of the kaurenoic acid on genotoxicity and cell cycle progression in cervical cancer cells lines". Toxicology in Vitro. 57: 126–131. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2019.02.022. ISSN 0887-2333. PMID 30822460. Retrieved 24 January 2021.
- al, D. Kian et (2018). "Trypanocidal activity of copaiba oil and kaurenoic acid does not depend on macrophage killing machinery | EndNote Click". Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie. 103: 1294–1301. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.164. PMID 29864911. Retrieved 24 January 2021.