Kazimierz Prószyński
Kazimierz Prószyński (4 April 1875 – 13 March 1945), born in Warsaw, Poland, was a Polish inventor active in the field of cinema. He patented his first film camera, called Pleograph (in Polish spelling: Pleograf), before the Lumière brothers, and later went on to improve the cinema projector for the Gaumont company, as well as invent the widely used hand-held Aeroscope camera.
 | |
| Born | April 4, 1875 |
| Died | March 13, 1945 (aged 69) |
| Nationality | Polish |
| Occupation | Inventor, Film Director |
Biography
Prószyński was educated in Poland and Belgium, active in Belgium, France, England, United States and Poland. He was the grandson of the photographer Stanisław Antoni Prószyński, who had been accused by Russians of placing patriotic symbols in the background of the photographs made in his atelier and was sentenced for that by the Tsarist Russia authorities. He was also the son of Konrad Prószyński, an active Polish educator, writer and publisher.
In 1894, Kazimierz Prószyński built one of the first movie cameras. This Pleograph, or apparatus for taking photographs and projecting pictures, was built before the Lumière brothers lodged their patent. Prószyński also produced several films in Poland at the beginning of the 20th century as well as creating an improved film projector shutter, the first hand held film-camera and devised a method of synchronizing sound and film tracks.
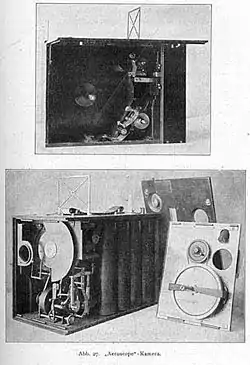
Kazimierz Prószyński spent a large part of his active life abroad. At the beginning of the 20th century, he was active in France and England as an inventor and producer of the Aeroscope (1909) camera, powered by compressed air. Filming with Aeroscope the cameraman did not have to turn the crank, as in all cameras of that time, so he had both hands on the camera to operate. This made it possible to film with a hand-held camera in most difficult circumstances and from airplanes. Compressed air was pumped into the camera system, before filming, with a simple special pump similar to the ones still used to pump bicycle tires. Hundreds of light and relatively compact Aeroscope cameras were used by British Army combat cameramen on the battlefields of World War I and later by newsreel cameramen until the late 1920s, when more modern spring cameras like Eyemo and later Bolex took over. Still, there are archival photographs of Aeroscope cameras being pumped by British combat cameramen as late as in 1940, at the beginning of World War II.
As soon as Poland regained its independence in November 1918, Prószyński returned with his English wife, Dorothy, and children Kazimierz junior and Irena. From the start it was difficult to find business partners for his invention. In 1922, he managed to establish a company Oko (Polish for: eye) to promote a simple amateur camera of his construction with the same name, which Prószyński intended to mass-produce for schools and the public. The economic crisis of the 1920s interrupted Kazimierz Prószyński's plans. He was busy with other inventions, such as simple home film projectors and reading machines for the blind, but did not manage to mass-produce any of them.
During World War II and the German occupation of Poland, German Gestapo police discovered his workshop. They arrested Prószyński and his co-worker under the accusation of conspiracy. Released after 10 days, Prószyński did not manage to remove all suspicion. He was chased by Gestapo and had to move often to avoid arrest. Finally on 25 August 1944, during the Warsaw uprising, he was arrested.
Kazimierz Prószyński died in the German concentration camp of Mauthausen in spring of 1945, as the prisoner number 129957, shortly before liberation.
Kazimierz Prószyński is regarded along with Bolesław Matuszewski as one of the most important pioneers of Polish Cinema.
Further reading
- Władysław Jewsiewicki, Kazimierz Prószyński, Interpress, Warsaw 1974, (in Polish)
- Alfred Liebfeld "Polacy na szlakach techniki" WKŁ, Warszawa 1966 (in Polish)
External links
- Kazimierz Prószyński on Who is Who of Victorian Cinema
- *Trailer of documentary "Kazimierz Prószyński - genius nr 129957" on YouTube
