Lanthanum barium copper oxide
Lanthanum barium copper oxide, or LBCO, was discovered in 1986 and was the first high temperature superconductor.[1] Johannes Georg Bednorz and K. Alex Müller shared the 1987 Nobel Prize in physics for its discovery.[2]
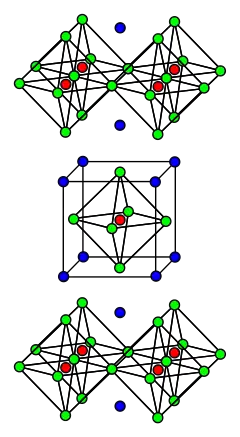 The unit cell of the layered perovskite structure of LBCO. Copper ions are red, lanthanum (barium) ions are blue, and oxygen ions are green. | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Ba2Cu3LaO7 | |
| Molar mass | 716.190 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- J. G. Bednorz and K. A. Müller (1986). "Possible high Tc superconductivity in the Ba−La−Cu−O system". Z. Phys. B. 64 (1): 189–193. Bibcode:1986ZPhyB..64..189B. doi:10.1007/BF01303701.
- Hazen, Robert M. (1988). The breakthrough : the race for the superconductor. New York: Summit Books. p. 255. ISBN 978-0671658298.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.