Laugier–Hunziker syndrome
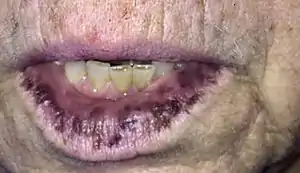
Laugier–Hunziker syndrome (/ˈloʊʒieɪ ˈhʊntsɪkər/) is a cutaneous condition characterized by hyperpigmentation of the oral mucosa,[1] longitudinal melanonychia,[1] and genital melanosis.[2]
| Laugier–Hunziker syndrome | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
The hyperpigmentation presented in Laugier-Hunziker syndrome is benign and should be differentiated from Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
See also
- Peutz–Jeghers syndrome
- List of cutaneous conditions
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.