Leslie Holdridge
Leslie Ransselaer Holdridge (September 29, 1907 – June 19, 1999) was an American botanist and climatologist. He was the father of composer Lee Holdridge.
Leslie Holdridge | |
|---|---|
| Born | Leslie Rensselaer Holdridge September 29, 1907 |
| Died | June 19, 1999 (aged 91) |
| Nationality | USA |
| Citizenship | USA |
| Alma mater | H. B.S. in Forestry, University of Maine, 1931, postgrad., 1931-32 M.S. in Ecology, University of Michigan, 1946, Ph.D., 1947. |
| Scientific career | |
| Institutions | Technological of Costa Rica |
Career
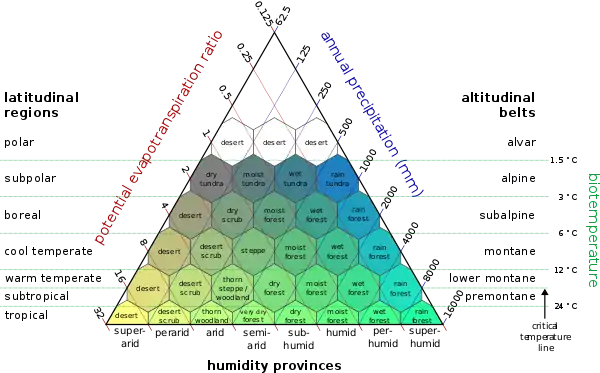
Diagram of life zone classifications.
In his famous 1947 paper,[1] he defined "life zones" using three indicators:
- Mean annual biotemperature (average temperature, after data values below 0 °C or above 30 °C have been eliminated)
- Total annual precipitation
- The ratio of mean annual potential evapotranspiration to mean total annual precipitation.[1]
Holdridge participated in the Cinchona Missions, a United States effort to search for natural sources of quinine during World War II.[2]
See also
References
- Holdridge, L.R. (1947). "Determination of world plant formations from simple climatic data". Science. 105 (2727): 367–8. Bibcode:1947Sci...105..367H. doi:10.1126/science.105.2727.367. PMID 17800882.
- Steere, W. (1945). The Cinchona-Bark Industry of South America. The Scientific Monthly, 61(2), 114-126. Retrieved from http://www.jstor.org/stable/18623
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.